Through looking at an essential nutrients role in health and its characteristics of deficiency, one can come to appreciate its value in good nutrition.
Vitamin K Role in Health
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in fat tissue and the liver. It is essential for building strong bones, preventing heart disease; as well maintains healthy blood clotting.
Characteristics of Vitamin K Deficiency
Arterial calcification, cardiovascular disease, varicose veins, osteoporosis, tooth decay and increased risk of infectious diseases.
Health conditions like Chron’s disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis and gall bladder disease; can prevent the body from absorbing vitamin K. Liver disease and blood thinners like warfarin can also lead also lead to a deficiency.
Vitamin K1 Food Sources
Vitamin K1 is found mostly in dark leafy green foods, herbs and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and brussels sprouts.
Nutrient-Rich Whole Food Sources for Vitamin K1
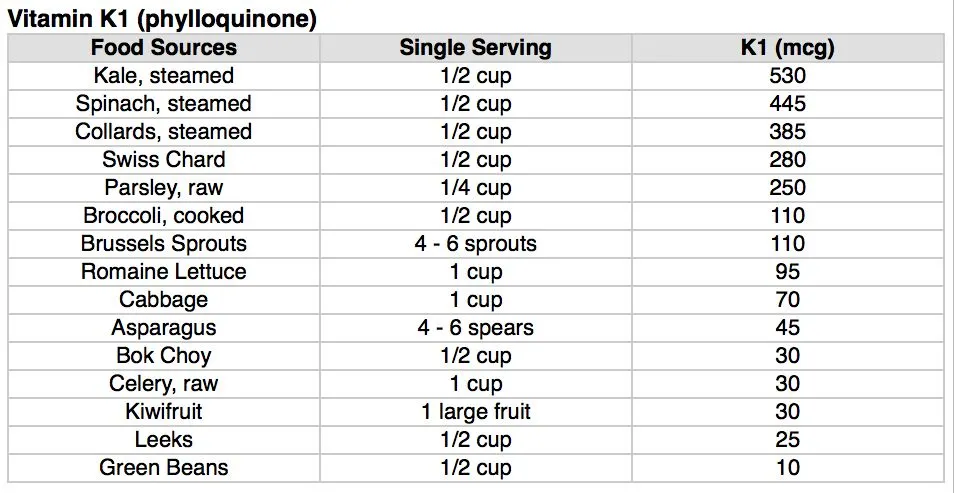
This chart lists the best food sources for vitamin K1, along with that food source’s single serving size and the amount of vitamin K1 in that single serving.
The amount of nutrients per serving in the following food sources is not absolute for several reasons. Fresh foods will have a higher vitamin and mineral content when grown in healthier soil, as well vitamin content will deplete a little bit every day from the moment it is harvested. Therefore, these figures should only be used as a general guide.
Vitamin K Daily Intake Recommendations for Child and Adult

These figures are referenced from the Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) 2005 system; used in Canada and the United States. The DRI system provides the minimum daily intake requirements of vitamins, minerals and nutrients for child and adult; males and females.
Written and shared by: J. Marshall from http://nutritionalhealingrecipes.com