Through looking at an essential nutrients role in health and its characteristics of deficiency, one can come to appreciate its value in good nutrition.
Vitamin E Role in Health
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that protects the body’s cells against free radical damage; which slows the aging process; and against diseases like cancer and heart disease. Vitamin E is also essential for the function of many organs in the body and for making red blood cells. Vitamin E is fat-soluble and aides in digestion and in the absorption of nutrients including helping the body use vitamin K.
Characteristics of Vitamin E Deficiency
A vitamin E deficiency can be characterized with muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass; as well abnormal eye movements and vision problems. A person may also become unsteady while walking when deficient. A long-term deficiency can result in liver and kidney problems. People with digestive disorders who cannot absorb fat properly are more at risk of a deficiency.
Vitamin E Food Sources
Vitamin E can be found in several different foods. Seeds and nuts provide an excellent source of this essential nutrient, along with dark leafy greens. Other good food sources include eggs, wheat germ, fish and a few vegetables.
Nutrient-Rich Whole Food Sources for Vitamin E
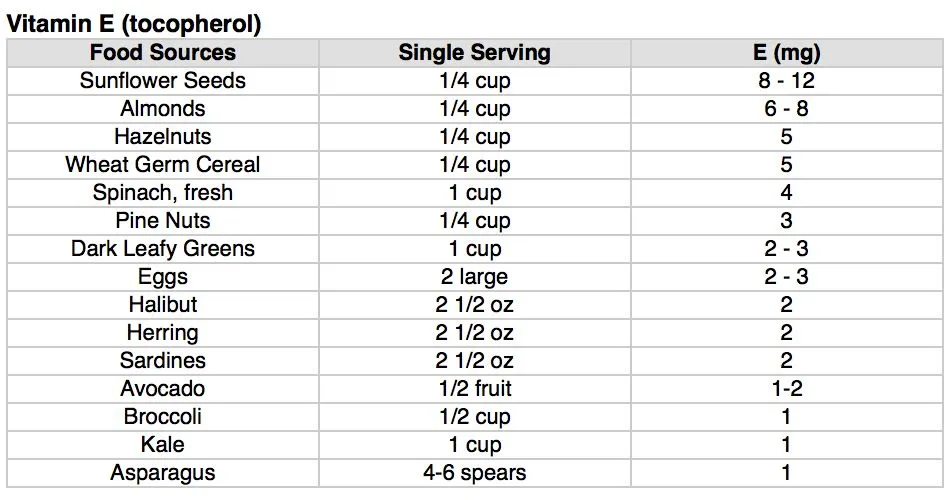
This chart lists the best food sources for vitamin E, along with that food source’s single serving size and the amount of vitamin E in that single serving.
Vitamin E Daily Intake Recommendations for Child and Adult
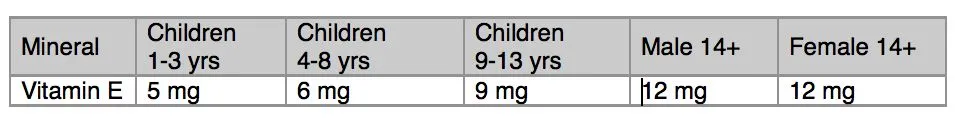
These figures are referenced from the Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) 2005 system; used in Canada and the United States. The DRI system provides the minimum daily intake requirements of vitamins, minerals and nutrients for child and adult; males and females.
Written and shared by: J. Marshall from http://nutritionalhealingrecipes.com