
What is xDAC?
Nowadays companies are confronted with many problems like rules and regulations of each jurisdiction separately. This causes a lot of bureaucratic work for the companies and in the end they waste time and effort for stuff that don’t advance the company’s processes.
xDAC wants to achieve a platform on which companies can create and manage their whole infrastructure and ecosystem and solve the problems we mentioned before.
With the help of decentralized ledger technology xDAC wants to give companies more freedom.
All xDAC companies are governed by same rules
This has the advantage that anyone can create and manage a company without any limitations, third parties, etc.
Also very interesting is that xDAC calls himself a subclass of DAO (decentralized autonomous organization), but what this really means, we are going to discuss later on.
How they want to achieve this vision?
They unite three components: governance, finances and workforce
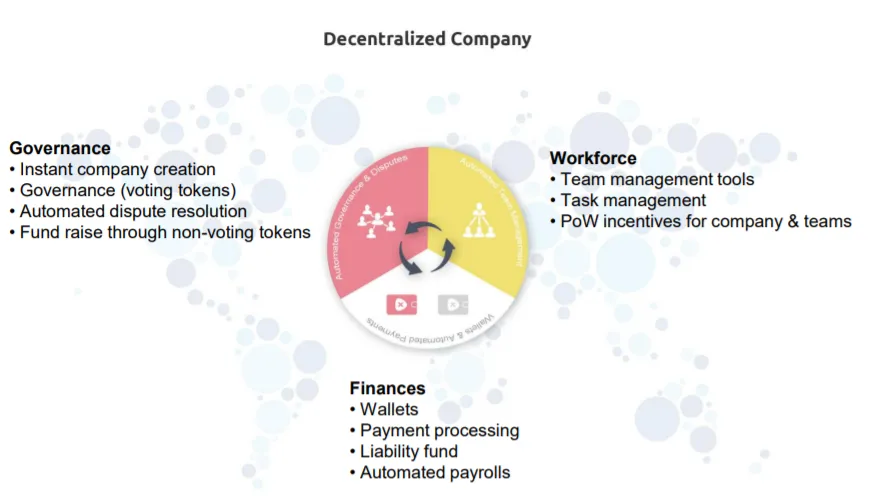
Through this, anyone can create a decentralized company instantly without fearing of judges, court proceedings, registration, or any financial institutions.
Start-ups have to fear of financial institutions which don’t share the ideas of the company. In this case financial institutions don’t want to cooperate and your project ends even before it has really started.
The Fundraising is regulated through ICOs. No bank accounts, merchant accounts, payrolls needed.
They want to develop the xDAX platform on the EOS platform.
Token Allocation
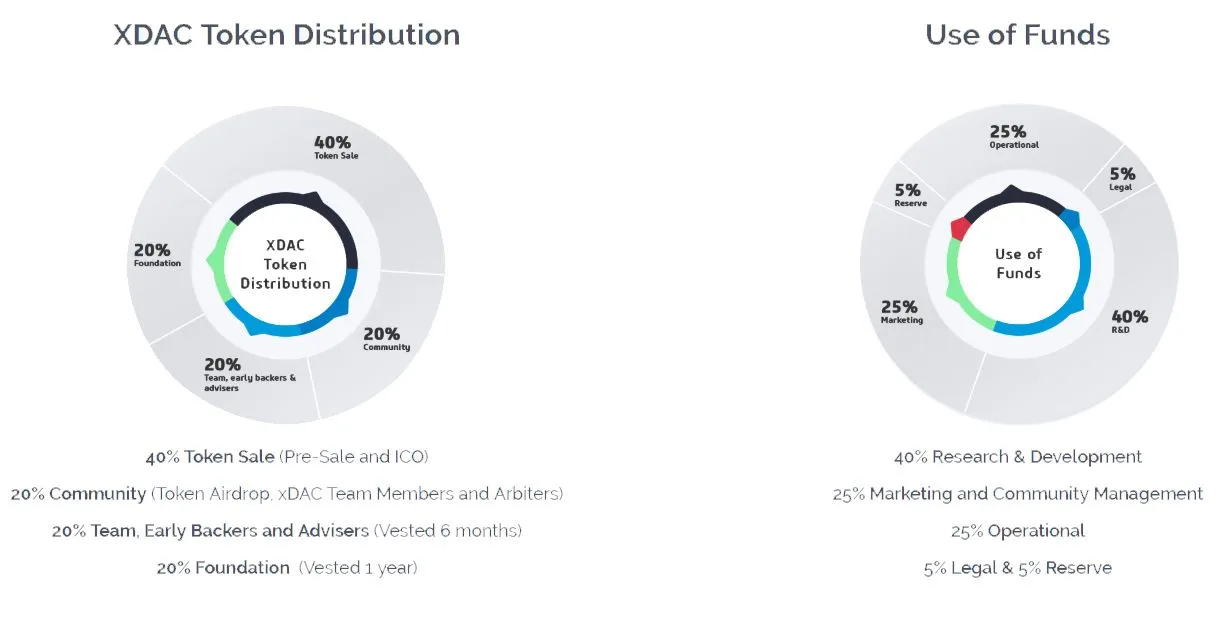
What are the tokens for?
- You can create your own company by using the platform currency.
- You can sell your products and accept the tokens as payments.
- Your team can be payed.
- You can create different funds like e.g for liability.
- You can distribute your profit by using tokens.
Roadmap

Governance
One of the most important components of the XDAC Platform is governance. XDAC wants to establish methods that develop trust for customers and business partners.
But what if conflicts or disputes between XDAC owners, customers, employees or other third parties appear?
In contrast to the traditional judicial system which can lead to high costs, XDAC wants to establish a new industry of independent arbitrators. They are supposed to solve disputes faster and more efficiently than existing systems.
Another feature of the XDAC platform is the freezing in real time, that will increase customers protection und secures users from further damage. The team wants to implement an automated system monitoring at all time to guarantee safety for customers and business partners.
In the white paper, XDAC analyzes a case with BitGrail exchange in which they show how their system would protect customers, users and business partners in such a case:
BitGrail became insolvent three months prior to ownership disclosing the truth. Customers were sending money to the exchange the entire time and most fiscal damages took place during the last three months. Customers were powerless, unable to freeze the company’s account, since the company ended up being outside of their jurisdiction.
i. Dispute Resolution
Any third party with payment history with xDAC can start dispute. If disputed amount is less than xDAC’s liability fund (see section 5.2.6), dispute can be resolved directly between both parties unless one party does not agree with the result and wish to escalate the dispute to Dispute Representative Board. In case disputed amount is larger than xDAC’s liability fund, company will be automatically frozen until dispute is resolved by voting of Dispute Representative Board.
ii. Dispute Representative Board and Voting
The Dispute Representative Board (DRB) is a group of at least five anonymous arbitrators (representatives) which are XDAC token holders. A quorum of 60% of all votes is required for any dispute to be resolved. Representatives are casting their vote based on documentation provided by both sides. 60% is needed to resolve any dispute. xDAC can set the per vote bounty for each dispute resolution and dispute will wait for resolution in the pool of disputes available to random representatives. Representatives will be paid per dispute in XDAC tokens. The higher the bounty for dispute resolutions the xDAC sets, the faster the dispute will be resolved as representatives will be looking for highest rewards. This results in expedient resolutions in the most objective way imaginable.
Any selected representative can review the dispute, vote on it accordingly and receive a bounty for resolution. Representatives can decide to resolve any dispute from a pool of disputes based on the bounty amount. If applicant or defendant does not agree with result, they can escalate dispute two more times until a resolution has been reached. Disputes will be resolved if 60% votes are reached in two out of the three hearingsiii. Assigning a Representative
xDAC has the ability to choose voting representatives on their behalf. This is a powerful decentralization tool that has no strong analog in Proof of Work or Proof of Stake protocols. In conventional PoS systems, the account owner’s node must be running to participate in voting. xDAC has the ability to reassign consensus to any account at any time. A change of xDAC representative is performed by subtracting the vote weight from the old representative and adding the weight to the new representative.
Further jurisdiction rules can and will be evolving continuously.
Automated rating systems
Based on Proof of Work:
Freelancers can store all profile and portfolio data on the blockchain, meaning there is solid proof of what they did. All work can be clearly attributed to the owner and information on copyright can be secured too. Ruling possible disputes between the client and the freelancer becomes simpler as all data is securely recorded.[1]
XDAC wants to take these advantages and transform the Team Member Rating(TMR) into the Team Rating (TR) and out of this calculate the Company's Rating (CR)
Team Member Rating (TMR):
Rating R = Range between 0 and 1
(0 for not #completed/ not delivered task or not paid on time)(1 if everything worked fine)
TMR= Sum (R) / Sum(Tasks)
Team Rating TR = (TMR1+TMR2+..TNRn )/n
Company Rating CR= (TR1+TR2+..TRn) /n
TMR can be seen as productivity rating and is in that way a recommendation profile for further assignments with other companies/teams.
TR is an indicator to compare Teams according to their performance.
CR is used to:
- Calculate platforms profit distribution
- Attract investors
- Show reliability
Whether a task has been executed and by when it must be executed is determined by the project management. The payout trough XDAC Tokens for the Team Member will then be automatically executed inside the XDAC Platform. Features will be further developed by the xDAC Foundation.
How does the xDAC Platform generate profits?
The whitepaper lists the following points to make profits:
- Transactions fees
- Exchange fees
- Fees for token creation
- Distribution through ICOs
How will the profits of the platform be distributed?
In order to split the profit among the companies, the respective share of the CR (Company Rating) is divided by the sum of all CR and multiplied by the profit.
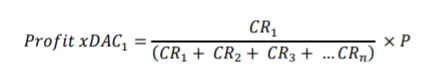
The distribution within a company is regulated by a distribution coefficient (DC), which determines the respective TMR and the Team Size (TS) as determining variables. And then we proceed in the same way as when distributing to companies.
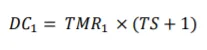
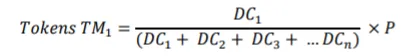
What is DAO?
The DAO was a digital decentralized autonomous organization, and a form of investor-directed venture capital fund.
The DAO had an objective to provide a new decentralized business model for organizing both commercial and non-profit enterprises. It was instantiated on the Ethereum blockchain, and had no conventional management structure or board of directors. The code of the DAO is open-source.
The DAO was stateless, and not tied to any particular nation state.
The DAO was crowdfunded via a token sale in May 2016. It set the record for the largest crowdfunding campaign in history.
The DAO was a decentralized autonomous organization that exists as a set of contracts among people that resides on the Ethereum blockchain; it did not have a physical address, nor people in formal management roles. The original theory underlying the DAO was that by removing delegated power from directors and placing it directly in the hands of owners the DAO removed the ability of directors and fund managers to misdirect and waste investor funds.
As a blockchain-enabled organization, The DAO claimed to be completely transparent: everything was done by the code, which anyone could see and audit.
Investors received voting rights by means of a digital share token, they vote on proposals that are submitted by "contractors" and a group of volunteers called "curators" check the identity of people submitting proposals and make sure the projects are legal before "whitelisting" them. The profits from the investments will then flow back to its stakeholders.
The DAO did not hold the money of investors, instead, the investors owned DAO tokens that gave them rights to vote on potential projects. Anyone could pull out their funds until the time they first voted.
xDAC takes this philosophy of DAO and improves it on its own way.
Resume
The Idea behind xDAC platform seems to be very visionary. Platforms like xDAC might become the future, cause xDAC closes the gap between blockchain and usability. “Mass adoption” is the Buzzword and this is what xDAC wants to achieve. The team has to proof if they well up on leading such a business like this. You have to consider that xDAC will be a long term investment, because building up an ecosystem of multiple companies cooperating on xDAC platform will in our opinion be an effort of minimum 5 to 10 years. Advantages and disadvantages appear through its underlying protocol EOS. On one side EOS comes with very fast transactions and no transaction fees but on the other side you must consider that EOS has no working product right now and we will have to wait and see how EOS is established in the market.
[1] Ralph C. Merkle, 2016: "DAOs, Democracy and Governance". Cryonics Magazine, JulyAugust, Vol 37:4, pp 28-40; Alcor.
https://www.forbes.com/sites/abdullahimuhammed/2017/12/15/can-blockchain-solve-the-common-problems-freelancers-face/#2989850312e8
visit: www.xdac.co for more information