Guys, I have been having a wonderful time writing on steemit, and I just can't stop. I just made an article yesterday and here I am today making another. Well do have a wonderful time as you read through.
This post is about the Moon. Imagine you are given a photograph of some object on Earth's surface taken from an altitude of 1000km. How would you try to identify the object? You would study the specimen and it's surroundings very carefully. Then you would use your observations to compare the object with a familiar object .Finally references about your observation will be taken. Scientists have used this techniques the Earth's Moon. The moon is about 348,400km above earth.

Image source:pixabay
The Lunar Satellite
There are dozens of artificial satellites that circle around the planet but the moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth.
At its surface, the moon's gravity is about one sixth of the earth's gravity. Now this implies that a person's weight on the moon will be one sixth of the weight on the Earth.
Astronauts have left many scientific instruments on the lunar surface. Data from these instruments on the lunar surface reveals that the moon doesn't have a magnetic field. Seismic instruments measure moonquakes and provide data about the moon's interior.

Image source:wikimedia commons
The lunar Surface
Exploration of the moon's surface has shown it to be barren and lifeless . Temperatures there may range from 130°C to -175°C at night. These evidence indicates there's no water on the lunar surface. Consequently there is no weather. The absence of water and an atmosphere means that no weathering of the lunar surface occurs. Therefore the rocks and rock formations have remained almost unchanged for much of the moon's history.
The most obvious features on the lunar surface is the circular indentations known as craters. Most of the moon's craters were created by meteorites striking the lunar surface. But some of the smaller ones may have volcanic origins.
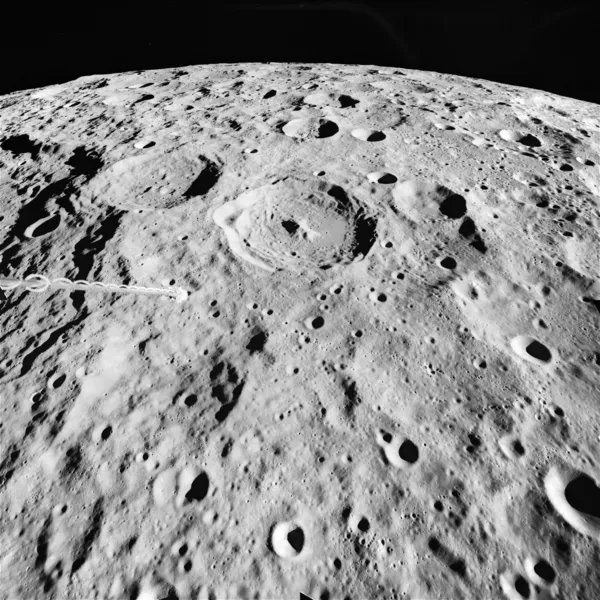

Image source:wikimedia commons
Moon's Movements
The moon has an elliptical orbit around Earth. The moon remains in its orbit because the gravity of the Earth and the gravity of the moon pull each other. The moon's closest point to the Earth is called perigee and the fastest point in its orbit is called apogee.
The moon's period of revolution is the same as its period of rotation. The moon completes one revolution in 27.3 days. During this period it also rotates on its axis. Because these two periods are equal, the same side of the moon always faces the Earth.
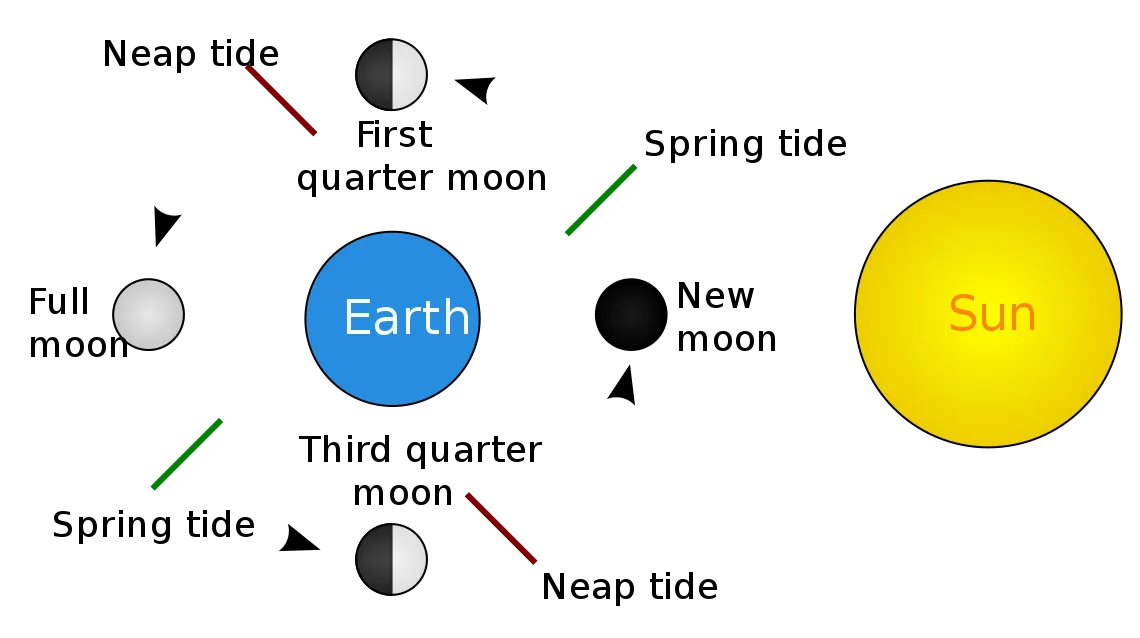
Image source:wikimedia commons
Origin Of The Moon
For years people have been wondering where the moon came from, though some theories have been developed, most of them have flaws.
The daughter theory suggest that a piece of split off to form the moon. However this theory doesn't explain why the moon is not composed of the earth's crust material.
The sister theory this theory states that the Earth and the moon formed from Gas and dust during the formation of the solar system. This theory can not account for the differences In the rock composition between two or more bodies.
The capture theory this theory proposes that the moon formed elsewhere and was capture by d gravitational force of the Earth as it passed. It is argued the moon wouldn't have attained a stable orbit without the assistance of a third body. No evidence of such have ever been found.
In 1959, the Soviet spacecraft Luna 3 radioed back the first photographs of the moon's far side. Motivated by the Soviet's success the USA began the Apollo project. The project goal Was to place an astronaut on the moon before 1970. On July 16, 1969, Apollo 11 was launched. Neil Armstrong became the first man to set foot on the moon. He was followed by Edwin Aldrin, Jr.
The two astronauts collected materials from the moon before returning to Earth.
Moon Machines
The machine that carries astronauts to the lunar surface is called the lunar module(LM). The lunar module is a small spacecraft that separates from the larger command module. The Lunar module has a separate fuel system that allows it to land and take off. The LM serves as the headquarters for the astronauts while they are on the moon, when the task is completed the lunar module leaves the moon to reconnect with the command module. The LM is later discarded into space. Even though the lunar module doesn't remain on the moon other machines brought to the moon are still on its surface. The Lunar Rover or moon buggy, is a battery powered vehicle similar to a funeral buggy. Instruments were also left on the moon to conduct scientific see experiments. The passive seismic experiment records moonquakes and meteorite impacts. The Lunar surface gravimeter detects changes in the gravitational field. The lunar atmospheric composition instruments analysis lunar gases. The data from these scientific devices are sent back to earth for analysis.
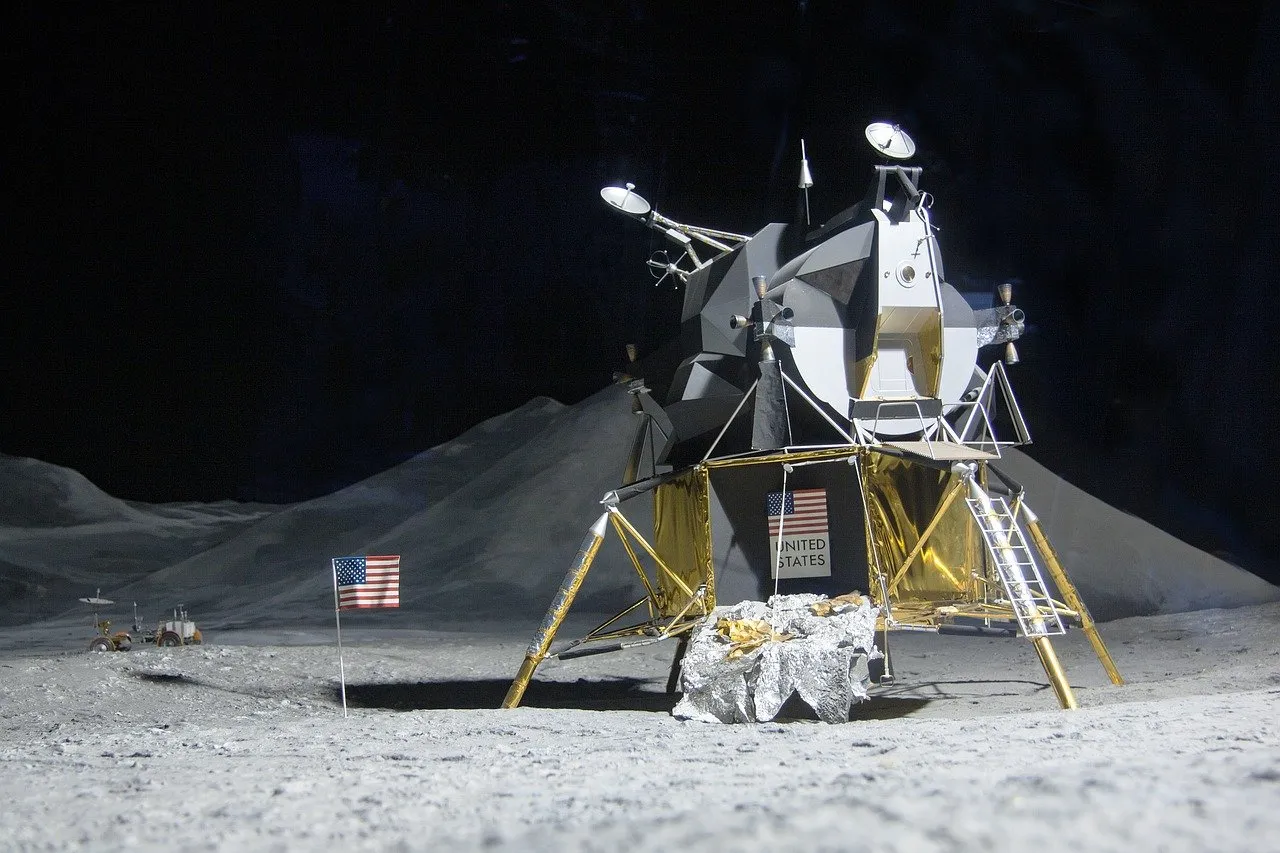

Image source:max pixel
Lunar module
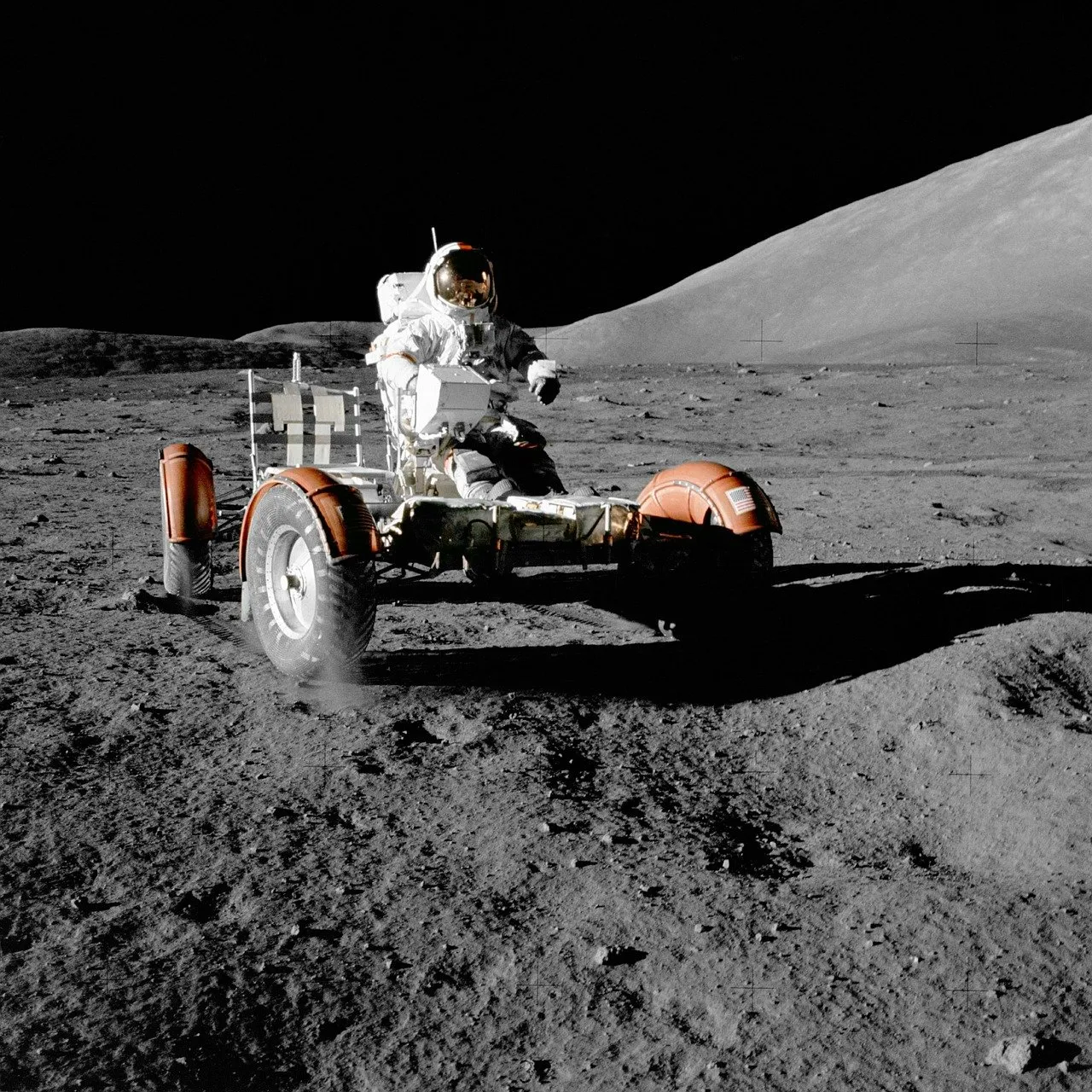

Image source:pixabay
Lunar Rover