This series of lectures will offer deep opening in-depth of how networks function and how they operate in practice and theoretically. For this season, after a while, I decided to go through my field of studies and that is Computer Networks.
I will be covering many topics in my subsequent article breaking down the OSI model, discussing on switches and routers, Servers, spanning tree, OSPF, stackable switches, VLANs, and also labs on them.
Introduction
The recent use of networks all over the world has produced communication around the globe. We can communicate without interference and interruption. The internet has opened a well where data can be stored and transferred from one place to another. Devices are manufactured by different manufacturers with the primary aim of spreading information and accomplishing assigned tasks.
Mobile devices are used by almost every individual. Unlike before, where mobile devices don’t have compatibilities to handle internet services. But as the world is growing in an extensible structure to the pattern of technology, we discover that series of jobs are done with our mobile devices. More compatibility in helping humans to do unimaginable jobs. Transferring data from one device to another.
When devices like printers, laptops, pc, and other peripherals of a computer are connected together, they form a computer network and this allows communication flow from one device to another.
Data Communication
Data communication specifies the transmission of data signals between computers either two or several computers. Thus we can say that computers exchange data.
When it comes to network or computer network, we can say that it is a telecommunication network which gives the computer the permission to exchange data.
Computers don’t just exchange data itself, they require a physical connection and that makes it possible for them to establish communication between themselves. Furthermore, when it comes to physical communication of networked computer devices, mediums of communication is essential. It can be a cable or a wireless mode of transmission.
Almost everyone knows the meaning of data as it is a raw fact that is yet to be processed and when it is processed then it is known to be information.
Data are represented by binary information in a computer system I.e: 1s and 0s. Data is the plural of datum and are sent through a communication channel.
Components of Data Communication
Before data communication is established, there are certain specific components that need to be available.
- Sender
- Receiver
- Message (Represented in blocks of bits)
- Networking Software
- Medium (This is the communication channel either wired or wireless)
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCES NETWORK
Geographical Factor
Around your environment, networks can be extended ranging from your Bluetooth device and any connected devices across your table that can be few meters away. The advances in technology have given us an edge and we can explore connectivity of various networking devices. For example in a company, the devices used are networked together so as to communicate to each other.
Networking is not only limited to building alone as a human is not limited to his friends in his/her immediate environment. A human wants communication especially to know and taste different environment. So is our devices in our environment. They want to communicate, they want to know more, and they want to perform at a high speed when supplied with components that make them compatible for performance.
Networks are extended across cities, provinces and now covered around the world. The network has travelled around the world and this has brought easy communication from one geographical area to another.
CONNECTIVITY OR TOPOLOGY
When devices are placed in any specific area, there is a need to adopt a pattern of connectivity that can either be logical, physical or the combination of both.
There are several pattern or structures used to identify connectivity when it comes to networking.
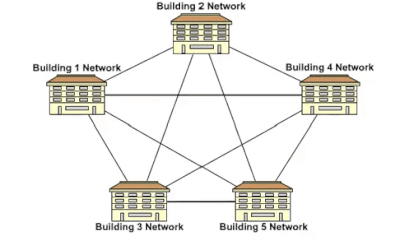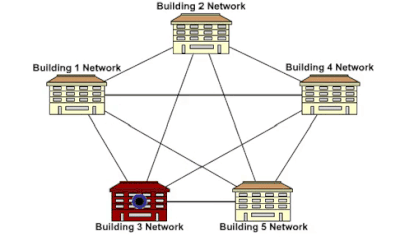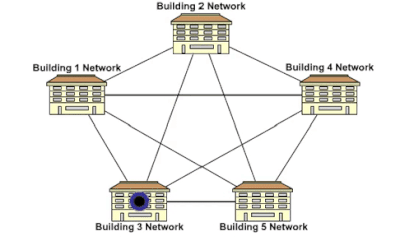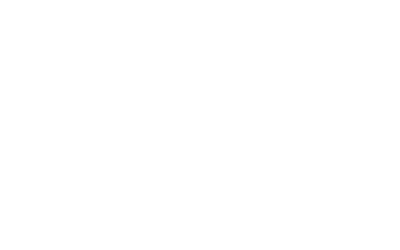
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology enables point to point connectivity between devices or nodes. In this kind of topology, each node is connected to one another.
Over mesh topology, two techniques are used and they are
Routing Mesh Topology: Communication is done using Routing logic. Data are directed to reach each destination using the shortest available distance. This routing logic holds information of failed nodes and tries to avoid it when carrying packets of data. Obviously, we can have the routing logic to re-configure or amend nodes that fails to co-operate with the topology.
Flood Mesh Topology: Data are transmitted to every connected node. This kind of network is robust and the usage of a routing logic is not required. However, it is unlikely to lose data when using this kind of topology. One of the negative aspects of using this topology is the fact that it overloads the network.
Types of Mesh Topology
- Partial Mesh: In this kind of topology, devices are connected with each other and some other devices are not connected to each other as they are viable of connecting to two or three devices.
- Full Mesh: Nodes are connected to each other
** Pros and cons of Mesh Topology**
Pros
- Each connection is responsible to carry the load of its data
- When a fault is found, it can be diagnosed easily
- Security is ensured and privacy is conserved.
Cons - The configuration is complex
- The cost of cabling is expensive.
Bus Topology
When we talk about bus topology, we talk about devices connected to a single channel or medium but in their structure, they are geographically disconnected. If the topology has two endpoints, it is known to be a Linear Bus topology.
Bus topology tends to transmit data just in one direction but in parallel because the networking devices are connected to a cable.
Pros of using a Bus topology
When building a networking environment it is necessary to have in mind the cost and the quality of communication medium in order to attain a high speed of transmission when nodes are communicating with each other. If you want to go for a topology that is less expensive, then you have to look into the Bus topology because the required cable is less compared to mesh and other listed topology.
Bus topology is used in a small networking environment and can be understood easily. Additionally, joining or connecting two cables is easy.
Cons of using a Bus topology
The problem of failure in the network is one of the things that any network administrator would not like to occur but in the lifeline of networks, it is inevitable. Because one way or the other there must be a network failure.
In the life of a Bus topology, when the single cable used fails to communicate, then the whole network goes down. This can happen in a split of seconds. It can be a rat that chewed the cable and when it does, the whole network will certainly go down and this will cause catastrophe.
If the incoming and outgoing network traffic is heavy, the performance of the network will decrease and this will lead to slow transmission of data packets from nodes to nodes.
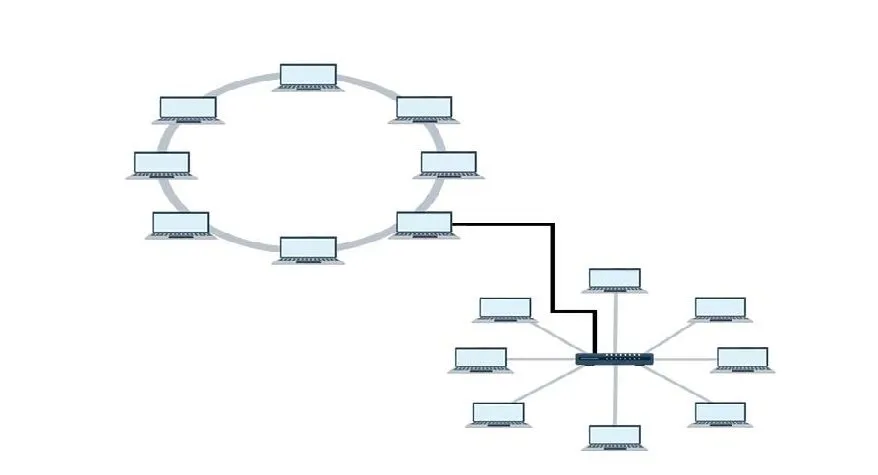
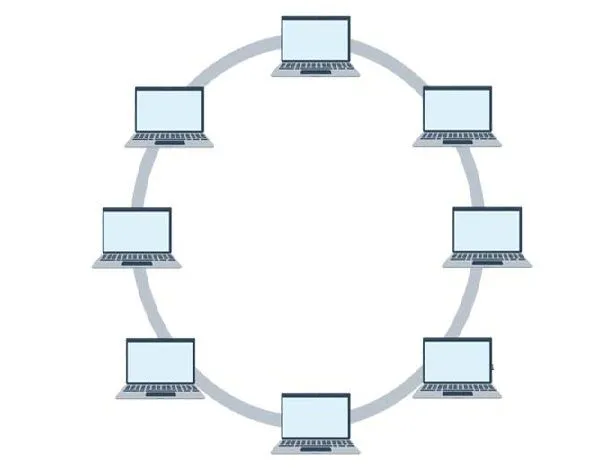
Ring Topology
Almost everyone knows what a ring is. In the genealogy of networks, rings are also considered and they are devices connected to form a ring. Each device connected has two neighbours.
Features
A large number of repeaters are used in ring topology especially when there is a quantified number of nodes in order to prevent data loss when transmitting data from a large distance (Several numbers of Nodes).
Rings are unidirectional but can be made bidirectional when a node has two connection. Thus it is called Dual Ring Topology. In a Dual ring topology, two certain rings are formed that are meant to flow in two opposite direction
** Pros of Using a Ring Topology **
Ring topology is less expensive to deal with and when transmitting data over the network, the traffic is not affected if nodes are added to the network.
Cons of Using a Ring Topology
The complexity of the topology makes it difficult for network administrators to troubleshoot and the failure of a single networking device brings failure to the whole network
Star Topology
In this topology, devices are connected to either a switch or a hub through a cable. The switch or the hub serves as a central node that connects to all devices.
Features
In this topology, fibre optic, coaxial cables or twisted pair cables are used. They are connected to a device and the switch/hub which serves as a repeater. Every single node respects its own identity.
Pros of Using Star Topology
Several nodes perform at high speed a there is a tendency of low traffic in the network. The modern world tells us of how switches can upgrade its firmware in order to perform at a quality state. This happens also while using the star topology.
Further, the modification and setup are not complex and the network tends to work effectively if any other node fails to work properly.
Cons of using a Star Topology
The cost of installation is very high and expensive and if the switch fails to work, all the network will cease to function but thanks to technology that has given us a chance to implement backup switches to our topology.
In addition to the cons, when it comes to switches and hubs, the performance of the network depends on the capacity of the switch. If the capacity of the switch is very low, then we should be expecting a low performance of from the switch.
Tree Topology
A brief explanation of the tree topology. This topology has a source where it spreads its wings across different computers. It forms a hierarchy amongst itself. Likely, they spread itself in three hierarchy.
Its feature includes a group of computers working together and its used mainly in wide area networks (WAN).
Hybrid Topology
When we eat bread without butter, how do we feel? Unlike when we eat bread mixed with butter or honey? This is also same with networks. Here two or more topology is combined together. It can be the combination of ring and bus topology or the combination of mesh and star topology. Thus it is called Hybrid topology.
Effectiveness, reliable in detecting errors and scalability are the main pros of this topology however, they are complex to design and expensive to install or setup.
So How Do We Apply Networks or How DO we see it In Our Daily Report
- The exchanging of emails from the sender to the receiver deals with networking schemes
- Sharing of resources using the web
- Connectivity of IP telephones
- Instant messages, a user accessing the internet and having the feeling of having different dynamic web pages being displayed.
Summary of This Part oF Computer Networks and Interconnectivity
No matter what you do don’t forget this part of understanding as they help you when it comes to the basic terms of networking
Data: the raw fact
Data communication: specifies the transmission of data signals between computers either two or several computers. Thus we can say that computers exchange data.
- Mesh Topology: Each node is connected to each other.
- Bus Topology: Devices are connected to a single cable
- Star Topology: Are connected to a central hub or switch.
- Tree Topology: Hierarchy topology that has a source device
- Ring Topology: They form ring…each device has two neighbours
- Hybrid Topology: Combination of two or more topology
Did you know?
- The internet is the popularly known network.
- The brain technology of the internet began way back in 1960 at MIT. It was there that the first ever transmitted and the message was the word LOG. The user tried to enter the word LOGIN but the network was interrupted.
Until the next episode of Computer Networks and Interconnectivity. Be successful. Be wise while spending your time.
References For Further Reading
Interesting Facts abot the internet
Topology Types
Classification Of Networks
Introduction To Computer Networks

 By
By  By
By