Perforation Methods
Once it has been determined that there is probably an oil field, the only way to find out is piercing. Drilling in search of Natural resources is not a concept new. In the year 1100 AD, drilled brine wells in China with depths of up to 3,500 feet, using methods similar to drilling per percussion.
source
• Percussion drilling: This is the method that the first ones used oil explorers ("wildcatters") in the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century, and still used today for some wells shallow The method employs a pipeline heavy steel drilling with a bit on the bottom, suspended from a cable. The method consists of lifting and releases the tool repeatedly. The metal mass falling on the bit provides the energy required to break the rock, opening a hole through it. The hole remains empty, except a small amount of water in the bottom. After drilling somehow many feet, the pipeline goes up perforation (with its bit) and the cuts with a bailer (one tube open with a valve in the bottom). He percussion drilling method is simple, but only effective in the wells shallow The progress of the work is very slow due to the inefficiency of the bit and the need to remove the tools often to extract the cuts.
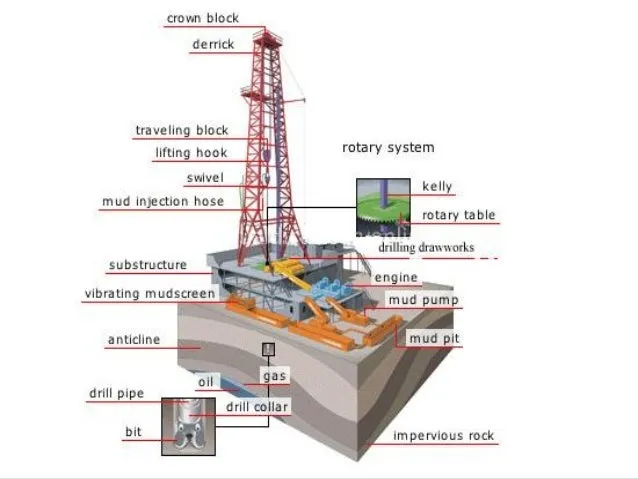
• Rotary drilling: The teams of rotary drilling are used for different purposes - drilling wells oil, gas, water, geothermal and storage of oil; extraction of nuclei for mineral analysis; Y mining and construction projects. Without However, the most important application is the drilling of oil and gas wells. According to the rotary method (introduced in Well drilling industry oil and gas around 1900), the bit is suspended from the extremity of a tubular drilling column (drill pipe) supported by a cable/block system which, in turn, is sustained by a derrick. The perforation occurs when the drill string is rotated and the auger, while the lastrabarrenas and the auger impose weight on the rock. To continuously cool and lubricate the drill and remove the cuttings from the hole, pumps a drilling fluid (mud) inside the drill column.
To the reach the bit, this mud passes through of the nozzles of the bit, collides with the bottom of the hole and then it goes up in the annular space (the space between the column of drilling and the wall of the well), carrying the cuts that are suspended in it. On the surface, it filters Mud with screens and other devices that eliminate the cuts, and then they it pumps again into the well. The circulation of drilling mud provides rotary drilling the efficiency that could not be achieved with the percussion drilling - the ability to remove the cuttings from the well without removing the pipe to the surface.
Bit
To describe the drilling equipment rotary, it is best to start with the where the action takes place - that is, the bit. By rotating under the weight of the Drilling column, the bit breaks or scrape the rock that is below. The first rotary bits were "Drag drills" because they scraped the rock. As they looked like the tail of a fish, received the name of "bits Fishtail". These drills were effective to drill formations soft, but their fins were worn quickly on hard rocks. Thus a better rotary bit was needed and at the beginning of 1900 the roller bit.
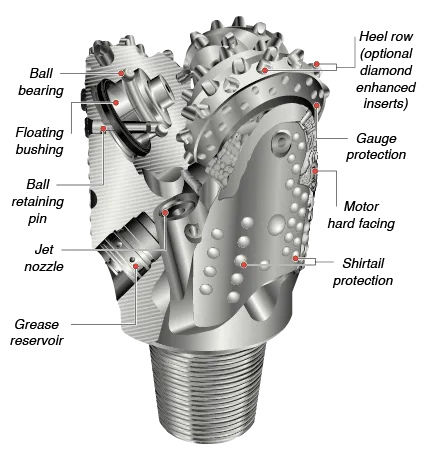
- Roller bits (for rocks): A roller bit - also called rock drill - has two or three strawberries conical that role as it is done turn the bit. The surface of the roller conical has teeth that go into contact with most of the fund's hole as the cones rollOver the surface. These drill bits drill fracturing the rocks hard and grooving the softest rocks. There is also an action of scraped because the axes of the cones are decentered in relation to the axis of rotation. The weight of the bit, the Rotation speed, the hardness of the rock, the differential pressure, and the speed and viscosity of the drilling fluid affect the penetration speed of the drills. The nozzles contained within of the body of the bit increase the mud speed, producing a jet when the mud leaves the bit. This contributes to a more perforation fast.
Rock drill bits are classified according to the types of bearings and teeth that they have Types of bearings include (1) unsealed roller bearings, (2) sealed roller bearings and (3) smooth bearings. When it is referenced to the bits based on the types of teeth that they have, the following are used terms: (1) insert teeth and (2) tungsten carbide drills (TCI - Tungsten Carbide Insert). The design of Bearing is important for the service life of a bit the sealed bearings and the smooth bearings provide a useful life longer than unsealed bearings, but they are more expensive. The teeth of a rock drill - its shape, size, number, and placement - they are important to ensure the effectiveness of drilling in different formations. The drills of milled teeth have teeth that are machined from the same ingot metallic than the cone. In some cases, the teeth are coated with hard metal to increase the service life.
This type is designed for formations soft to medium hard where the Long teeth can groove the rock. The teeth of toothbrushes of inserts are actually asparagus tungsten carbide inserted in holes drilled inside the cones. The TCI drill bits drilling generating an action of crushing for harder formations and more abrasive. Some toothbrushes of inserts are improved with inserts specials characterized by the application of a polycrystalline diamond layer of tungsten carbide. This will provide an even longer life than tungsten carbide alone.
source
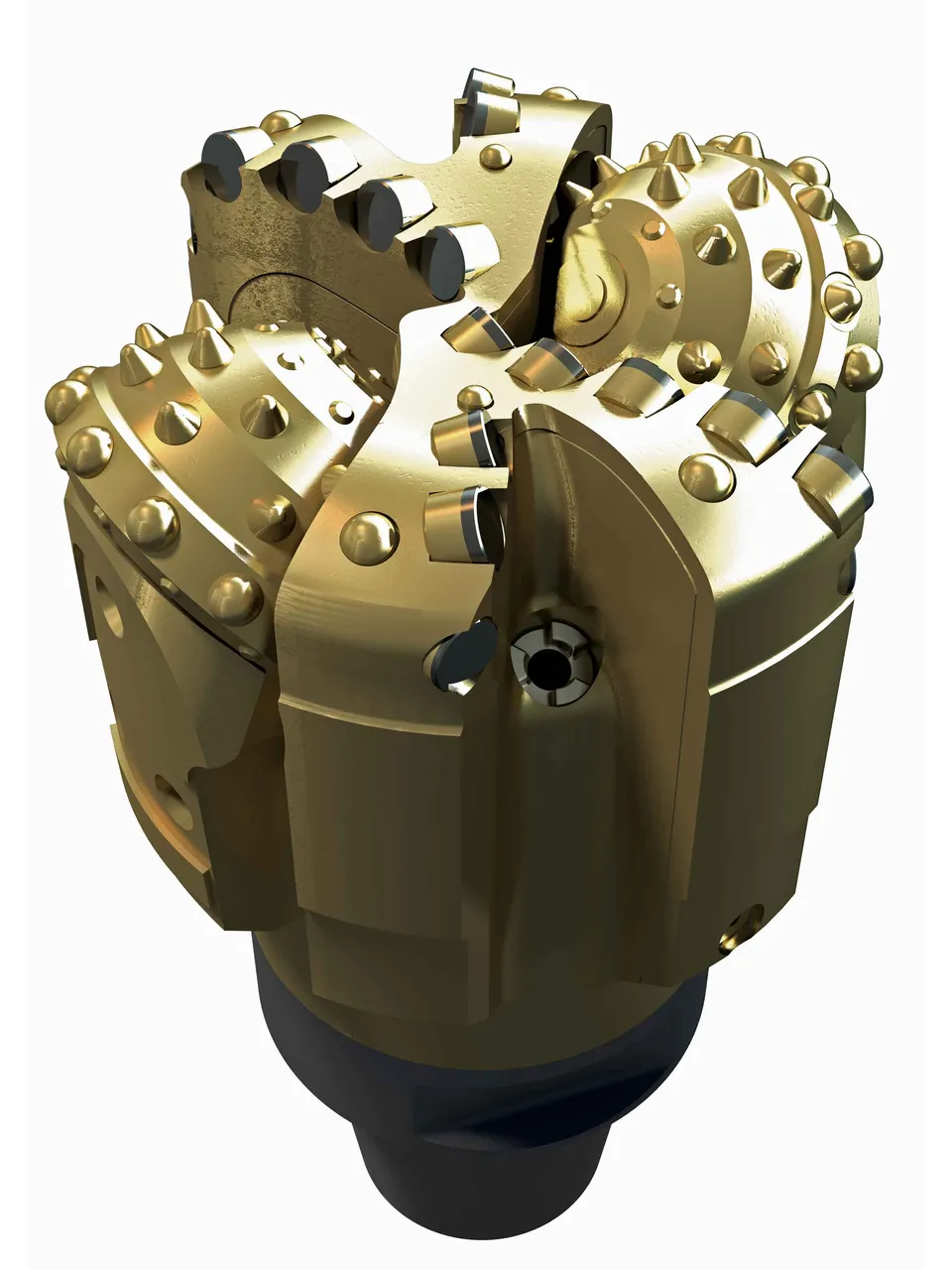
• Diamond drills and PDC: The fixed cutter bits with surfaces diamond cutters are used for formations drilling moderately hard to hard, when requires an extra-long life of the bit, or for special operations of extraction of nuclei. The drills of fixed cutters in one piece use fragments of natural diamond or pills of synthetic diamond as cutters. Natural diamond bits use industrial grade natural diamonds arranged in a steel matrix. During the rotation, exposed natural diamonds scrape and they crush the well. The cutters of synthetic diamonds, called Cutters of Polycrystalline Diamonds (PDC), are configured so that the Cutters break by shear stress the rock that is below the bit, producing large cuts and great penetration speeds. The PDC bits have the great demand to drill in many types of rocks, but especially in long sections of formations moderately hard to hard. The drills PDC's are very durable and effective, offering higher speeds of penetration and a long lifespan. HE manufactures PDC bits from different designs to optimize drilling in particular formations. Typically, PDC drills drill with greater quickness in the shales than in the sandstones, and they are used more frequently to Drilling long sections of shale. Both of the types of diamond drill bits work in a similar way to the old "tail of fish" drag bits because they drill by scraping the rock.

source
The Perforation Column
Starting in the background, a column Basic drilling for drilling Rotary consists of (1) the bit, (2) Stanchions and Bottom Sets (BHA - Bottom-Hole Assembly), and (3) pipes of drilling.
The Fund Set is located just above the bit and is composed of portamechas combined with one or several fin stabilizers (for maintaining the Fund Set and the concentric bit), possibly a stretcher (to avoid tapering of the well as the diameter of the bit wears) and other tools. The MWD tools (measurement at drill) and the back-end engines are generally located in the part bottom of the Set of Fund, just above the bitt. Sometimes it is placed a game of "hammers" near the part Top of the Background Set. The hammers can release the stuck pipe generating a hammering action when they are activated by a strong tensile stress.
The portamechas are heavy tubes of the thick wall that are used in the Set of Fund to provide weight to the auger. In general, one of The drill holders is made of non-magnetic metal so that you can use a magnetic compass tool (lifting tool) for determining the set tilt Bottom bottom and auger without suffering the interference produced by the magnetic metals.
Each section of drill pipe it has a length of approximately 30 feet, with a female connection welded on one end and a connection male at the other end. These threaded couplings (pipe joint drill) must be strong, reliable, resistant and safe. They must be easy to screw (connect) and unscrew (disconnect). The outer diameters of the drill pipes are between 2 3/8 and 6 5/8 inches.
The hollow drill column provides a means for circulation continuous and to pump the mud from high-pressure drilling through the nozzles of the bit, producing a fluid jet. The jet of mud clears the area below the bit cuts, offering a new surface of the rock to the cutters, and start the return of drill cuttings towards the surface. This transmission of hydraulic power of the mud pumps the bit is a very important function important of the mud.

source
- Drilling with the flexible pipe: East method employs a continuous column of flexible pipe and a drill rig specialized for drilling with pipe flexible. Instead of drilling with different drill pipe joints rigid traditional large diameter, the Drilling column consists of a Flexible tubing with a smaller diameter. Unlike the drill pipe that must be screwed to form the drill column and that should be disconnected in bundles of standing pipe, placed in the derrick during maneuvers (ascent and descent of the pipe), the pipe is rolled in a reel that unwinds as you the perforation is advancing, and then rewind on your reel during the maneuvers. The flexible pipe method considerably facilitates the descent and Recovery of the drill assembly. Traditionally, teams of drilling with flexible tubing were used in rehabilitation operations and completion where mobility and Compact sizes were important. After the development of back-end engines in the bottom of the well, which does not require the use of a drill string rotary to rotate them a bit, the flexible tubing units are now functioning as real teams of drilling.
• Rotating table and kelly: A table rotary is a turntable powered by gears and chains, mounted on the floor of the drill rig, which has a large central opening for the bit and the drilling column. The joint bushing Kelly of the rotary table is a great Metallic "donut" with a hole quadrilateral, hexagonal or octagonal in its center. This bushing can accept a pipe special quadrilateral, hexagonal or octagonal, called kelly. The joint bushing kelly at the rotary table spins the kelly, whose length is approximately 40 feet, in the same way, that it is spun a hexagonal nut with a key. The kelly can freely slide up and down on the kelly board bushing, from the way it can be lifted while that a section of pipeline is connected 30-foot piercing (the highest joint of the drill column) on your part lower. Then the pipeline is lowered drilling into the well, until the bit makes contact with the bottom, and can rotate the kelly. The driller puts running the rotary table, and as you the drill goes drilling, the kelly also slides down. When the end of the kelly reaches the bushing level (at a level of the team floor), the kelly is disconnected from the drill pipe and lifted while another stretch is added, after which the process of drilling. So the mud of perforation can enter the column of drilling, a hose is connected perforation and a rotating union in the part superior of the kelly, to supply the mud to from the mud pumps. The Union Rotary is a hollow device that receives the sludge from the vertical tube and the hose from perforation, transmitting it through a rotary seal to the kelly and inside the drilling column. One drawback of kelly configuration/rotary table is the fact that while the pipe with the kelly disconnected, I do not know Can pump no sludge and rotation of the pipe is minimal.

source
• Traveling Rotarian: A unit of a Rotarian traveler presents considerable advantages on a control unit by Kelly/rotary. The Rotarian unit traveler spins the column of Drilling with a large hydraulic motor mounted on a sliding mechanism at the top of the tower drilling. Instead of drilling with a 30-foot stretch before making a connection, the traveling Rotarians use "Triples" of 3 drill pipe together (90 feet) and reduce considerably the number of required connections, as well as the time needed to make a maneuver. One of the key advantages – the driller can spin the pipe, going up and down over a distance 90 feet inside the hole, and do circulate the mud simultaneously. This allows expanding quickly and easily long and narrow sections of the hole without clog the pipe. Because of these advantages, Rotarian units are being installed traveler in most teams of Deep piercing and platforms drilling offshore.
• Background engine: While the two first methods of rotation assume the rotation of the drill pipe for the spin the bit, this method is different. In this case, an engine is mounted Hydraulic (bottom motor is driven by a turbine or positive displacement) in the Bottom Set, near the bit. During drilling, the energy Hydraulic produced by the passage of mud go through the motor spins the bit. This It is achieved through the use of multiple rotor/stator elements inside the motor, which rotate an axis to which the bit has been connected. This offers several advantages The back motors can achieve rotational speeds of the bit much larger than those can be achieved by spinning all the drilling column. Is required less energy to spin only the bit The well and the pipeline coating remain in better conditions, as well as the column of perforation when only the bit (and not the pipe). The major's rotational speeds (RPM) of the bit produce better Speeds Penetration (ROP) and reduce problems generated by vibrations. The back motors are in use extended in directional drilling where it is critical to maintaining the position of the orientation tool in the direction desired.

source
For more information visit the following links:
- http://wiki.aapg.org/Well_completion
- https://cdn.dal.ca/content/dam/dalhousie/pdf/faculty/engineering/peas/MEngProjects/2012MEngProjects/Jawad%20Farid%2C%20IMPORTANCE%20OF%20PERFORATION%20PROCESS%20AND%20ITS%20TECHNIQUES.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perforation_(oil_well)