Hello everyone

Images Source: Own by the author
I. Introduction
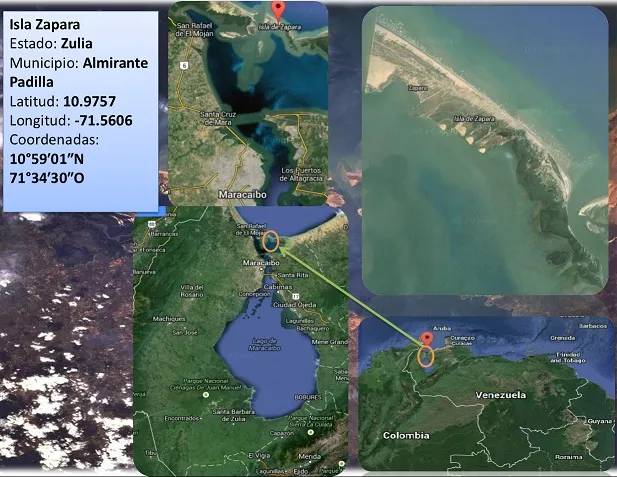
In Venezuela, as in other parts of the world, there is the presence of islands. We have, for example, the case of the Zulia state, which has its own islands within its geographical territory. One of these islands is called Zapara Island. The island is located within the geographical framework of the municipality of Almirante Padilla, with an area of approximately 7 square kilometers. In addition, it has a vegetation that stands out, presents some dunes that can reach about 30 meters. At the same time, it is taken into account to do research on the part of the universities.
In the zapara island, it is possible to visualize zones distributed by their characteristics, considering their vegetation. We can find: Primary dunes, secondary dunes, active dunes, a part that is in contact with the mangrove, among others.
We can find around 20 families of plants and about 33 species. One of the family is the Poaceae, around the world they have around 9000 species, presenting a great importance for the ecology, some studies indicate that this family was formed in the southern hemisphere during the geological epochs of the Oligocene and the Miocene. In addition, they are mostly plants of the herbaceous type, they can be perennial or annual. The flowers can be grouped to form structures called spikelets.
The other family of plants that are found in greater proportion are the Cyperaceae, just as the Poaceae are cosmopolitan, they have around 3500 species distributed. They are known as herbs that can be annual or perennial, with simple leaves and small flowers, sometimes the fruit may be wrapped by the bracts.
Images Source (edited): <a
href="https://www.google.com/maps/place/Isla+de+Zapara/@10.9612305,-71.5898973,13z/data=!3m1!4b1!4m5!3m4!1s0x8e8912c421f218c7:0xd80002d48227bfa8!8m2!3d10.971948!4d-71.5575586">Google maps
Some plants belonging to the vegetation of the island are:
- Blutaparon vermiculare; it belongs to the Amaranthaceae family, we can also find it in Texas and Florida (United States). They are perennial plants.
- Pluchea sagittalis; a plant belongs to the family Asteraceae, can measure up to 1.8 meters, has a strong stem and in many cases branched, in the United States it was considered a weed. Habitat normally in humid places.
- Heliotropium curassavicum; one of the names in the United States is Chinese pusley, this plant is common of very alkaline soils, it is normal for beach sands. It is a perennial herb.
- Polypremum procumbens; this is the only species of the genus Polypremun, it presents several seeds inside the fruit and is a perennial plant.
- Cenchrus ciliaris, in Venezuela it receives the name of "cadillo bobo", in other parts it is known as "buffalo grass". It is a perennial plant, reaches an average height of 1.5 meters, has barbs that develop throughout the year, the spikelets are arranged in bunches of cylinders and surrounded by a ring that adheres to the seed. According to some reports, it is possible that it arrived in the United States in 1946 and in Venezuela in 1950. It belongs to the Family Poaceae.
- Sporobolus virginicus; it is a Poacace, a perennial plant, with enough leaves, distributed over a large part of the land, although it is commonly found on beaches and dunes.

Images Source: Own by the author
- Fimbristylis spadicea; belonging to the Cyperaceae, is a perennial herb, has rhizomes.
- Sesuvium portulacastrum; it is a plant of the family Aizoaceae. It is a succulent and perennial herb, which is distributed on many coasts of the planet. It has a height of approximately 25 to 30 centimeters, it is known that the leaves are "fleshy" and are soft and thick, like the stem. The flower is pretty with a purple color.
- Fimbristylis cymosa; a perennial plant, a well-composed inflorescence, presents a resistant and subterranean rhizome. Habitual of beaches and dunes.
- Avicennia germinans (L); it is a mangrove with a great ecological importance, plant of great height can reach the 16metros of height. The leaves can have an oblong shape, the flowers are grouped.
II. Observations and discussions
The island of Zapara is considered as a coastal system, on the one hand they have the constant entrance of water from the Caribbean Sea and, on the other hand, the reserve entry into the mangrove. The latter has an important ecology, since they inhabit a great variety of organisms, such as crabs, dragonflies, migratory birds and those that are typical of the geographical area, among many others. Understanding the above is important because every factor that interacts on the island plays an important role. The vegetation to be exhibited in different geographical areas within the island, presents a form of adaptations to propagate that are subject of study, each species occupies an ecological niche or a specific area.

Images Source (edited): Google maps
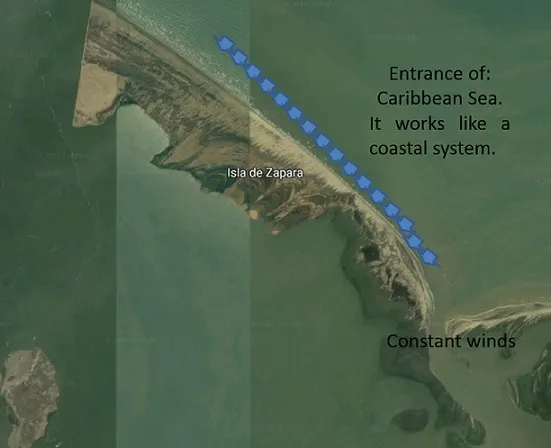
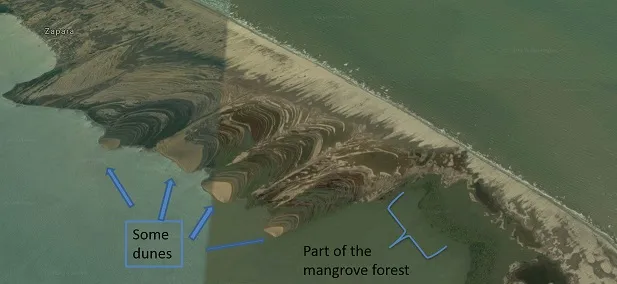
On the island it is possible to denote a sequence in the composition of the plants, for example, it is normal to find, first Cyperacea, second Sporobolos virginicus (as we see in the photograph), and a very close species Fimbristylis spadicea. Each of these perennial plants has characteristics of being "psamófilas", this means that they are plants that present an adaptation to sandy soils, with salinity due to contact with the sea. The studies, mention that the psamófilos can be located not only in low biological communities, but in dense spaces, also can occupy the areas in which they are not flooded in their totality by the marine water. This is consistent with what is observed on the island, the presence of taxa with similar morphological and physiological characteristics. This is evident due to the abiotic factors that are found.

Images Source: Own by the author
Several biological populations of herbaceous plants with halophytic and psamophilic characteristics occupy their ecological niche commonly in the littorals. In addition, it is worth mentioning that these species are found in normal coastal areas with salinity from the south of the United States to regions of Argentina, distributed in a similar way throughout the coastal zones of Venezuela. As mentioned, these communities have very similar characteristics, this is due to the conditions exposed on the coasts. For example, it is known that dunes come to be formed by wind currents, continuous waves and the grouping of sand.
In the muddy part of the wetland, we can find the species fimbristylis spadice, which lives together with other halophytic herbs. On the island,, it is remarkable that there is a strip composed of plants, xerophilous conditions, as well as muddy parts due to the entry of rain and water. In the mangrove, the damage caused to the leaves by the insects is appreciated. In other studies, it has been pointed out the presence of a considerable variety of animals that live in the mangrove and that feed on it. For example, the presence of the species Coelidia sp is visible in the leaves not only of the mangrove of this island but of other parts of the world. Other species of insects found associated with the mangrove are: Spissistilus festinus, Nasutitermes sp, Saissetia coffeae, Coptoborus pseudotenius and many more.
Images Source (edited): Google maps

Images Source: Own by the author
It is notorious the sequence of plants, depending on how you look, for this case we have the species Sesuvium portulacastrum, after the Sporobolus virginicus and near the dunes to Fimbristylis cymosa. The closer to the dunes, the vegetation is scarce. One of the proposed ideas is the pH level of the soil, the adaptations of the plant, the deployment of the roots, and the closer to the dune the nutrient resources are lower. In effect, there are several scenarios that we can propose.

Images Source: Own by the author
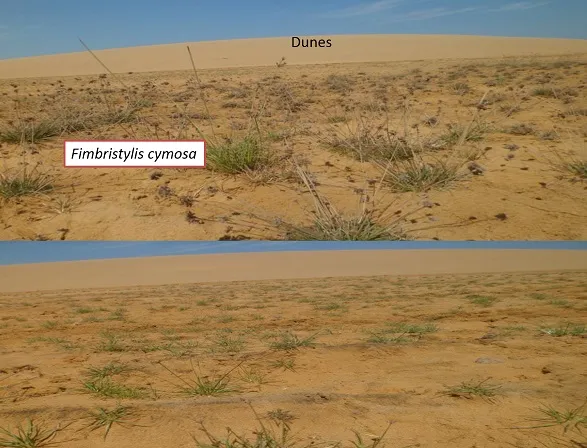

Images Source: Own by the author
It is also observed near the dunes, a dwarf mangrove, these comunmete grow when the soil has few nutrients, so they have a short stature, in addition this type of mangroves are represented by Rhizophora mangle and Avicennia germinans, have small leaves. The soils in which they grow are very saline. One of the possible reasons for this growth is likely because the area where it developed was flooded most of the year, by the entry of water. Then, due to solar initiation, this area remained with little water and more humid, to the point of being dry. In addition, it is likely to have a high level of calcium carbonate and make it difficult to obtain nutrients for the plant.

Images Source: Own by the author
III Considerations
- The coastal ecosystem often presents adversities for plants or any other organism. In addition, like any geographic area or biome, it has characteristics that affect the type of species that can be developed. For the case of the Island of Zapara, it has plants that present similar phenotypic adaptations, which has its evolutionary history.
- Characteristics such as soil with few nutrients, saline solution and very saline soils, the continuous entrance of saline water, some consider that there is little availability of water as it is filtered in the soil and with the solar incidence the water evaporates.
- At the moment, there is distribution and sequence of plants present on the island, which is reviewed by other researches. For all the above, it is possible that due to the same conditions of the plants and the island, is the explanation of the distribution or the sequences that can be seen.
Information reference:
- The Cyperaceae of La Selva Biological Station, Costa Rica
- Floristic survey and key to the species in IRBR Herbarium from halophilic and psammophile coastal land grasslands in Sucre state, Venezuela
- INSECTOS ASOCIADOS AL BOSQUE DE MANGLE EN BARRA SALADA, SONSONATE Y BAHIA DE JIQUILISCO, USULUTAN, EL SALVADOR
- Floristic composition, environments and vegetation on Zapara island, state of Zulia, Venezuela. Vol. 48. Nº 1, Enero-Abril 2014, Pp. 1 - 20. Boletín del Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas. LUZ.
- Herbotecnia
- Filogenia y evolucion de las Poaceae
- Herbario de la Universidad Publica de Navarra