The Studies of James Watson and Francis Crick on the molecule of ADN, with the skill of diffraction of x-rays, they allowed them to know different information on the dimensions and the structure of the molecules, it is formed by two spiral chains wound about the same axis. The linkage between nucleótidos takes place of such form, that the groups phosphate are joined with carbono5'de the pentosa of a nucleótido and carbono3 ´ of the pentosa of the following nucleótido, the pentosa and the groups phosphate constitute the skeleton of the helix, where they place the base towards his interior that's why his form dextrógiras and antiparallel, the diameter of the helix is constant, of such form if the bases join púricas of a chain with the pirimidímica of other one.
The only possible unions had to be citosona-guanina and adenina-timina, the sequence of the bases in a chain does not seem to have any restriction, whereas the sequence of the second chain is determined for being the complementary one of the first one.
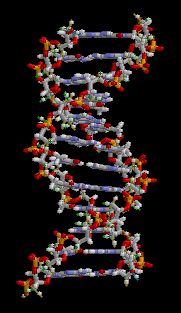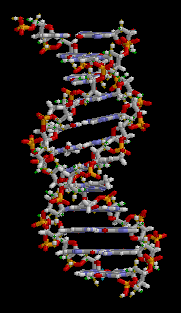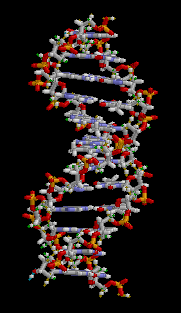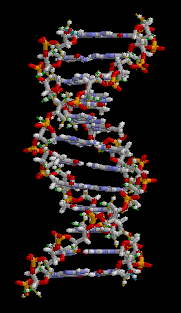
Animation on behalf of a structure of ADN of double helix, source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons
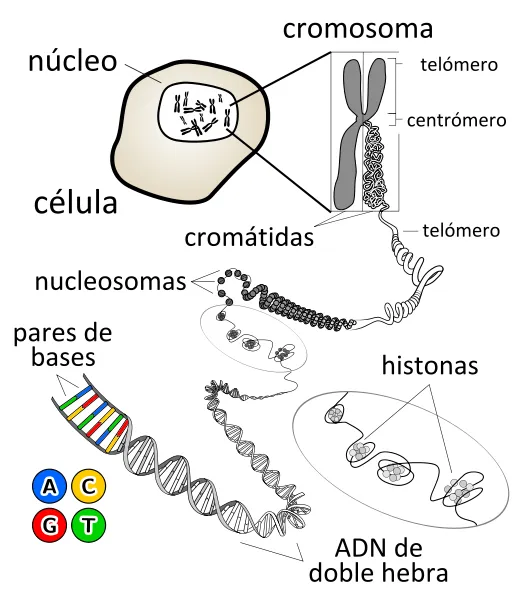
Situation of the ADN inside an eucariota cell, source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons
The quantity of chromosomes is own of every organism. The human beings have 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes compared to the fern Ophioglussum recitulatum with 630 pairs or 1260 chromosomes, the plant with more chromosomes that are known.
The chromosomes are composed of many genes, which take charge ordering by the instructions, so that the proteins start working, for the formatación and functioning of the organisms. The sequence of the base in a chain does not seem to have any restriction, whereas the sequence of other one is for being the complementary one of the first one, also during the cellular cycle, they double before the cell splits.
 Source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons Source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons | James Dewey Watson (Chicago, April 6, 1928), is an American, famous biologist for being one of three discoverers of the molecular structure of the ADN in 1953, together with the British biophysicist Francis Crick, and the chemistry Rosalind Franklin what cost him the recognition of the scientific community across the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
 Source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons Source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons | Francis Harry Compton Crick, OM, FRS (June 8 of July 1916-28, 2004), was a physicist, molecular biologist and neurocientífico British, known especially for being one of three discoverers of the molecular structure of the ADN in 1953, together with James Dewey Watson and Rosalind Franklin |
The organisms eucariotas for example, animals, plants and fungi, store most of his ADN inside the cellular nucleus and a minim divides in cellular so-called elements mitocondrias, and in the plastos and the organizing centers of microtúbulos or centríolos, in case of having them; the procariotas organisms, bacteria and you arch, they store it in the citoplasma of the cell and finally, the viruses ADN do it inside the cápside of protein nature. There exist multitude of proteins, like for example the histonas and the factors of transcription, which join the ADN providing it with a three-dimensional certain structure and regulating his expression.
The factors of transcription recognize regulatory sequences of the ADN and specify the rule of transcription of the genes. The genetic finished material of a chromosomal endowment is named genoma and, with small changes, it is typical of every species.
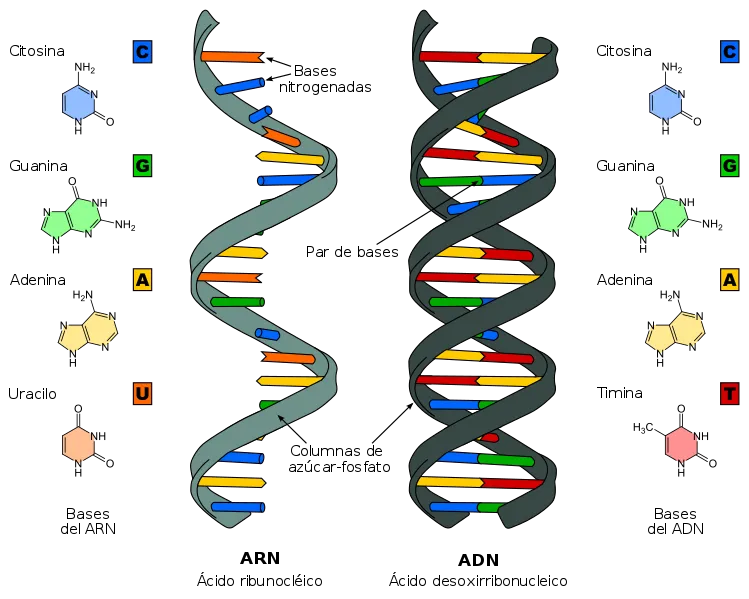
Comparative between ARN and ADN, source image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons
Make use also of the opportunity to comment on ARN, where the ribonucleic acid is formed to just as the ADN, for two bases púricas and two bases pirimidímica, but it is different for the timina one does not find in everything ARN'S species, but the base presents anyone also pirimidímica uracilos. Although, in some viruses ARN, they can take the genetic information to equal, that does it the ADN, in the cells procariotas and eucariotas, the fundamental mission of ARN, that is of trasportar a genetics keep in the chromosomal ADN, from the nucleus up to the citosol, where it will be translated to synthesize proteins.
different types of ARN Exist, each of which has structures and functions very specific in the expression of the genetic function of the cells and the types of messenger we have: ARNm, ARNr and of transference the ARNt, in contrast to the ADN, ARN'S molecules, are usually of simple chain and do not form double extensive helices, nevertheless, in the regions with bases paired yes it forms helices as structural tertiary motive.
An important structural characteristic of ARN, who distinguishes it from the ADN, is the presence of a group hidroxil in position 2 ' of the ribosa, which causes that ARN'S double helices adopt a shape A, instead of the shape B, that is the most common in the ADN, this helix A, it has a major rut much deep and narrow and a minor wide and superficial rut, the second consequence of the presence of saying hidroxilo, it is that the linkage fosfodiéster of ARN of the regions, in which one does not form double helix is more capable of hidrólisis chemistry that those of the ADN; the linkage fosfodiéster of ARN hidrolizan rapidly in alkaline dissolution, whereas the linkage of the ADN is stable.
Bibliography
Essentials of structural biochemistry - Page 277 FOR José Maria Teijón - 2006.
Biology: concepts and relations - Page 187 FOR Neil A. Campbell - 2001.
General Biology - Page 117 FOR Julián Monge-Nájera - 2002.
