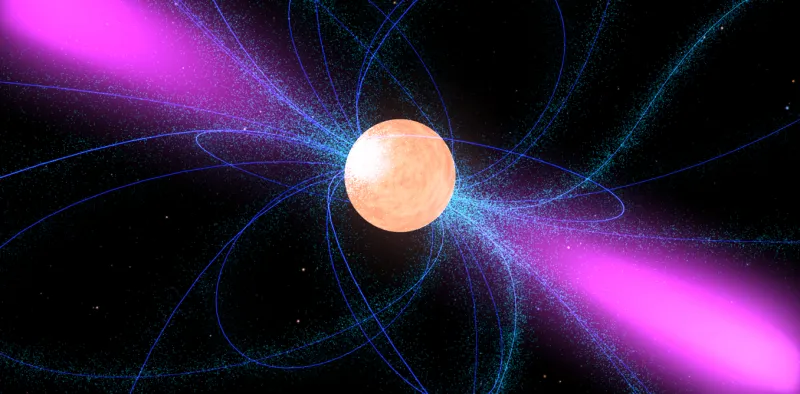
Neutron stars are the remnants of supernovas. They are incredibly dense, with a mass greater than the Sun but a diameter of only about 10 miles. Neutron stars rotate rapidly and have a strong magnetic field.
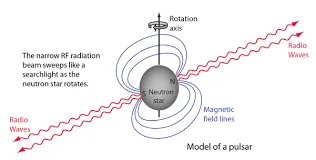
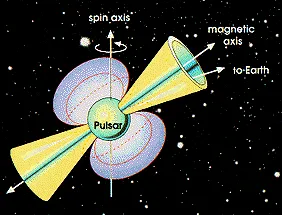
Pulsars are a type of neutron star. They emit a beam of radiation that is only detectable when it points directly towards Earth. As the pulsar rotates, the beam of radiation sweeps across the sky like the beam of a lighthouse. Pulsars are a type of neutron star. They are rotating neutron stars that emit a beam of electromagnetic radiation. As the neutron star rotates, the beam of radiation sweeps across the sky like the beam of a lighthouse.
Pulsars were first discovered in 1967. Since then, many more have been found. In fact, there are now over 2,000 known pulsars.
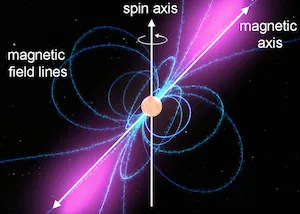
The Connection Between Neutron Stars and Pulsars
Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have exploded in supernovas. These stellar remnants are incredibly dense, with a mass greater than the Sun but compressed into a sphere that is only about 20 kilometers in diameter. And because of their immense gravity, neutron stars typically spin very rapidly.
Pulsars are a type of neutron star that emits a regular pulse of electromagnetic radiation. These pulses are caused by the rotation of the neutron star, which sweeps a beam of radiation around like a lighthouse beam. As the beam rotates, it is occasionally seen by observers on Earth, resulting in a pulse of radiation that we can detect.
Pulsars are fascinating objects, and they can teach us a lot about the Universe. For example, by studying the pulses of radiation emitted by pulsars, we can learn about the rotation and magnetic fields of these ultra-dense stars. We can also use pulsars to study extreme physics, such as the strong gravity near a black hole.
How Can Neutron Stars and Pulsars be Used?
Astronomers often use neutron stars and pulsars as tools for observing and understanding the universe. This is because these objects are some of the most extreme and fascinating objects in the cosmos. Neutron stars are the dense remains of exploded stars, while pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars that emit a beam of light.
Because of their strange properties, neutron stars and pulsars can be used to study a variety of astrophysical phenomena. For example, they can be used to study the effects of extreme gravity, the behavior of matter under extreme conditions, and the nature of the ultra-dense matter that makes up these objects. Additionally, pulsars can be used to study the properties of the magnetism in the universe.
So while neutron stars and pulsars may seem like strange and dangerous objects, they are actually valuable tools for understanding our universe.
How Can You See Neutron Stars and Pulsars?
Neutron stars and pulsars are some of the most fascinating objects in the Universe. These ultradense objects are formed when massive stars go supernova, and they can spin incredibly fast - as fast as hundreds of times per second. But what does that mean for us here on Earth?
Well, for one thing, it means that we can see neutron stars and pulsars in a way that we can't see any other type of star. When these objects spin, they emit a beam of light that can be seen from Earth. And because they spin so fast, that beam of light appears to be pulsing. That's how we get the name "pulsar."
Read more on:
Physics:
https://phys.org/news/2017-06-neutron-stars-gps-deep-space.html
Hyperphysics:
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Astro/pulsar.html
Nasa:
https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/objects/neutron_stars1.html