It's a lovely evening over here with cooling and bone chilling weather. It's harmattan season here.
Today's discussion will really bother on some core concepts and elements of quality that are necessary for sustainability of any organization that has a long term goal of providing quality health care. Our discussion will be within the premise of the health sector and little extension to biomedical engineering. So in essence, some definitions in this write up might not be exactly the same when you are discussing other works of life.
Quality management system is one very key important feature of a sustainable and reliable system. Any organization that doesn't have its foundation build on quality (degree of excellence) is bound to crumble over time. When we talk about quality, we mean those conscious step taken to ensure that our results are of standard and have high degree of excellence. Quality management ensures that a process is the same anywhere around the globe and also places priority on customer satisfaction.
Ever wondered why most carbonated drinks and infact all manufactured products either have exactly the same attributes especially when it comes to consumables. The soft drink you buy today will taste the same as one you would probably buy tomorrow provided it is strictly produced under International organization for standardization (ISO) guidelines. Without quality, product consistency and similarity in content cannot be achieved.
The truth remains that, quality is a way of life and you cannot do without it. You would recall I had the course to go for an ear investigation and the diagnosis was ear waxification. So in this discourse, I will explain in details the procedure and what causes ear waxification, how you can possibly prevent it and how proper to go about it. Let's get on with it shall we.
As I said in the previous post I made, I was experiencing some weird sound in the right side of my ear. Initially, I thought maybe it was water that managed to find its way, maybe through bathing perhaps. Usually, I am not always perturbed because I believe it will sort and later find its way out as usual, but this time, it's a different case. One month has passed, two months, now it's the third month, and it still persist.
I had the course to visit a Federal Medical Centre in the capital of where I am currently on a National assignment to do an ear examination. As one who is already in the field, I needed no one to show me the way around the hospital because, by standard, all hospitals have unique departments that operate and attend to different patients cases.
There is a particular unit that as a patient, and provided you are sound in health and you were able to come to the hospital yourself, you will likely pass through them first. This unit is the General Outpatient Department (GOPD). Virtually all standard hospitals established in Nigeria are structured this way.
Since I was a visiting guest, the standard protocol is to open a folder with the hospital. At this stage, your essential details like age, sex, next of kin, etc. are collected and documented in the hospital's database. After this stage, the main process to see the doctor then begins and at this point, you have to go through the nursing station.
In the nursing station, your vitals body parameters are very important, hence collected. Vitals include your body temperature, blood pressure, weight, heart rate (measure by counting the number of pulses detected and this is done by placing an index finger on the radial artery located around the wrist).
As a medical professional, I am not naive to all the processes I passed through. I only got concerned after checking my weight on the weighing scale. The reading recorded was quite lower than what I do weigh and I was confident that I have added in weight because I have not really been involved in much strenuous and mentally draining activities (mostly research studies).

Smart electronic weighing scale
I sensed an error in the reading, so I had to re-weigh in my facility. On getting back, I weighed and observed a remarkable difference in the values, and this proved me right, the weighing scale in the hospital was either faulty or not calibrated! Let's start with some basic definitions and concepts, this will help us alot.
Medical Equipment calibration
As one who is very conversant with the use of biomedical equipment, one very important question that one must be ready to answer at all times is - is the equipment giving the right result? The answer to this question alone will determine a whole lot of things.
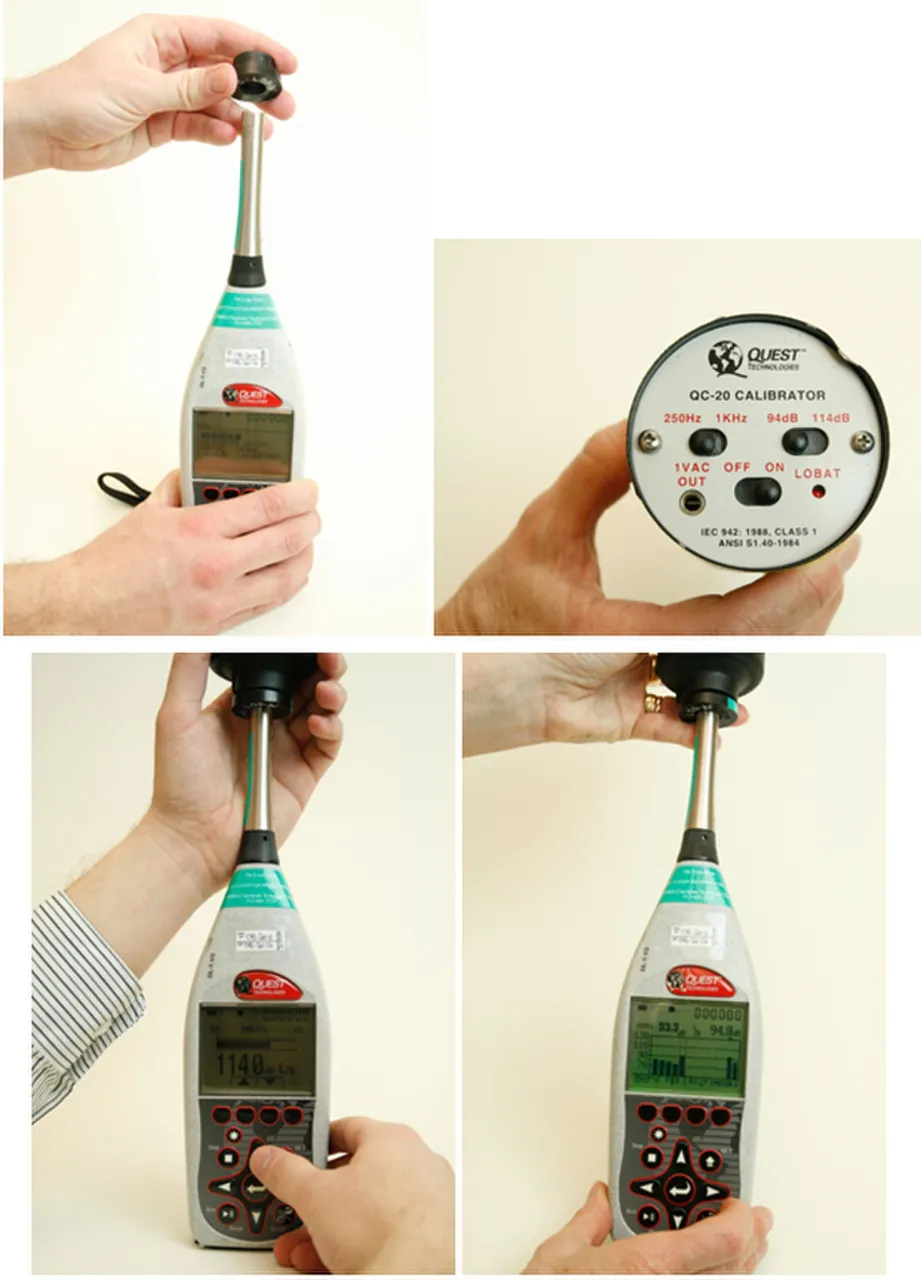

Calibration of a sound level meter
For example, if the answer is NO, then why? When last was it calibrated? Why hasn't it been calibrated? Who does the calibration? Is the person competent enough? Is the equipment used rightly according to the manufacturer's prescription? These are some of the questions most independent auditors do ask when on inspection.
Calibration is the process of comparing a reading on one piece of equipment or system, with another piece of equipment that has been calibrated and referenced to a known set of parameters.
Equipment calibration is simply the process of ensuring that a machine actually delivers on what it is claimed to do. Before a device can be said to be in full functionality, it must consistently give precise and also most importantly accurate results at all times if all things being equal (we will discuss precision and accuracy later on). It is done to confirm that an instrument delivers the right output at all times.
ISO varies depending on the industry it is required. For example, in diagnosis and medical sample handling, the required ISO type is ISO15189. For calibration or certification bodies, the ISO required is ISO17025.
ISO/IEC 17025, General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories, is the international reference for laboratories carrying out calibration and testing activities around the world.
When an equipment refuses to pass calibration, the implication is that, its reliability and validity is questioned. For an instrument to be certified ok, it must pass necessary quality checks. One very important advantage of equipment calibration is that, the results or output generated for any particular test or process will be the same anywhere provided the conditions of operation are the same condition.
Calibrating most equipment depending on what they are used for, all have one thing in common - standard. A standard is anything at all, be it a solution or a solid whose concentration or value of measurement is already known. The key word here is known concentration or value. Standards are used in comparison against the unknowns.
General rule of thumb in calibrating any instrument of any kind, be it medical or otherwise; you use the known to find and balance the unknown.
If a substance which is well known to have been confirmed to weigh Xg and then it is measured with a new equipment somewhere else, it must also weigh same.
Any discrepancy in value will sure raise concern on the reliability of the new equipment. The results may vary to some extent within allowable range limit, this can be accepted because of the impact of environmental conditions. But significant difference or a higher coefficient of variation in the result gotten, will sure raise concern.
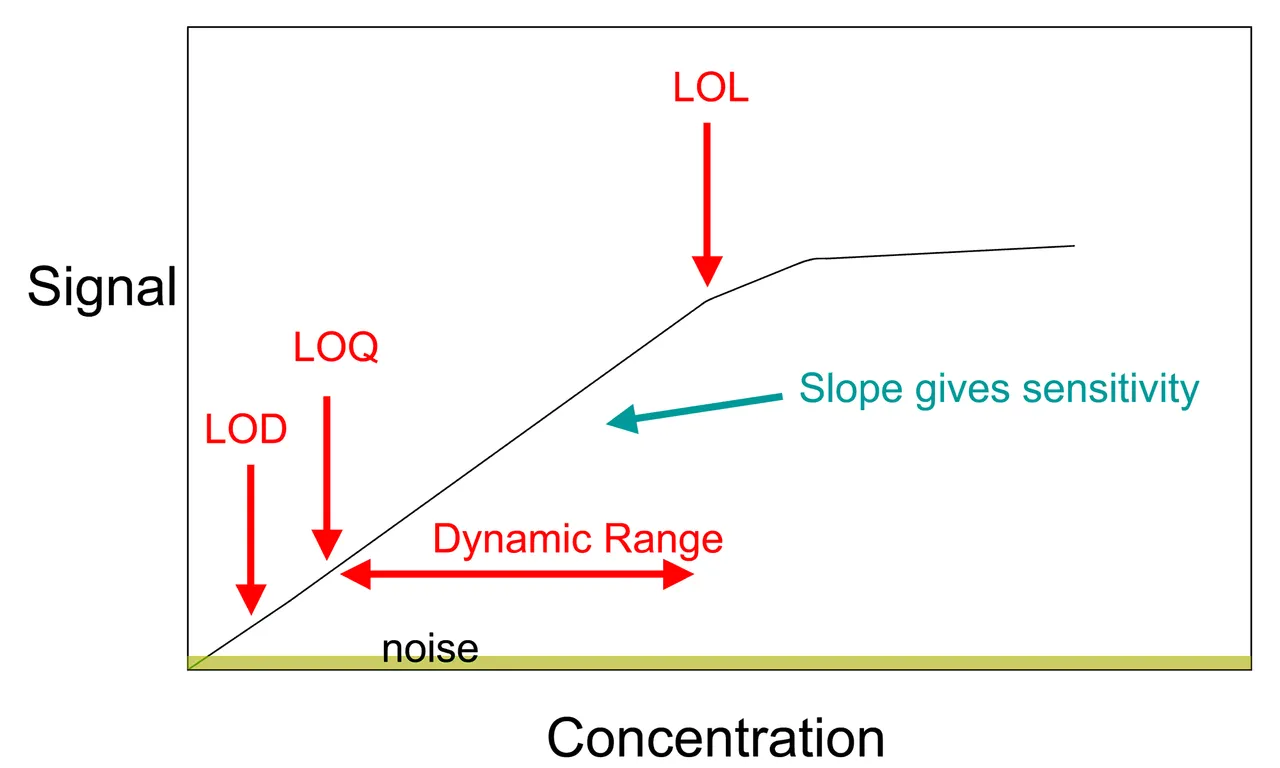
One of the ways to have a quick visual knowledge of how well a calibrated instrument is performing or has performed is to plot a calibration curve. The calibration curve will give you a quick understanding of the pattern of the equipment different result output, this of course is is dependent on the what is fed to the equipment, that is, input.
At limit of detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification, any measurement made cannon be trusted because at this point, it is where the medical equipment's ability of detection and Quantification is zero. At this limits, they are the zone of zero confidence in the resulTS produced.
Calibration of a medical equipment doesn't stop at using standard, controls - positive and negative controls are also very important, in addition, the sensitivity and specificity of the procedure or equipment also matters a lot. This brings us to the concept of sensitivity and specificity - the major indicators of equipment accuracy. Let's briefly discuss this concept.
Sensitivity and specificity of equipment
The word sensitivity simply means the ability to detect or sense the presence of a measurand (substance being measured). When we now narrow this down to equipment, it then means, the ability of that machine to detect that a substance of interest is present. It is the ability of the machine to detect even the presence of minutest concentration of the measurand.
When sensitivity is defined in relation; (either in percentage or proportion), then we can define it as the percentage/proportion of the analyte that is accurately identified as being positive (truly positive) and it also contains the measurand. So in essence, we are more interested in the presence of the analyte we are looking for. Sensitivity simply answers the question; is it truly there? Reason why is also referred to as true positive (TP).
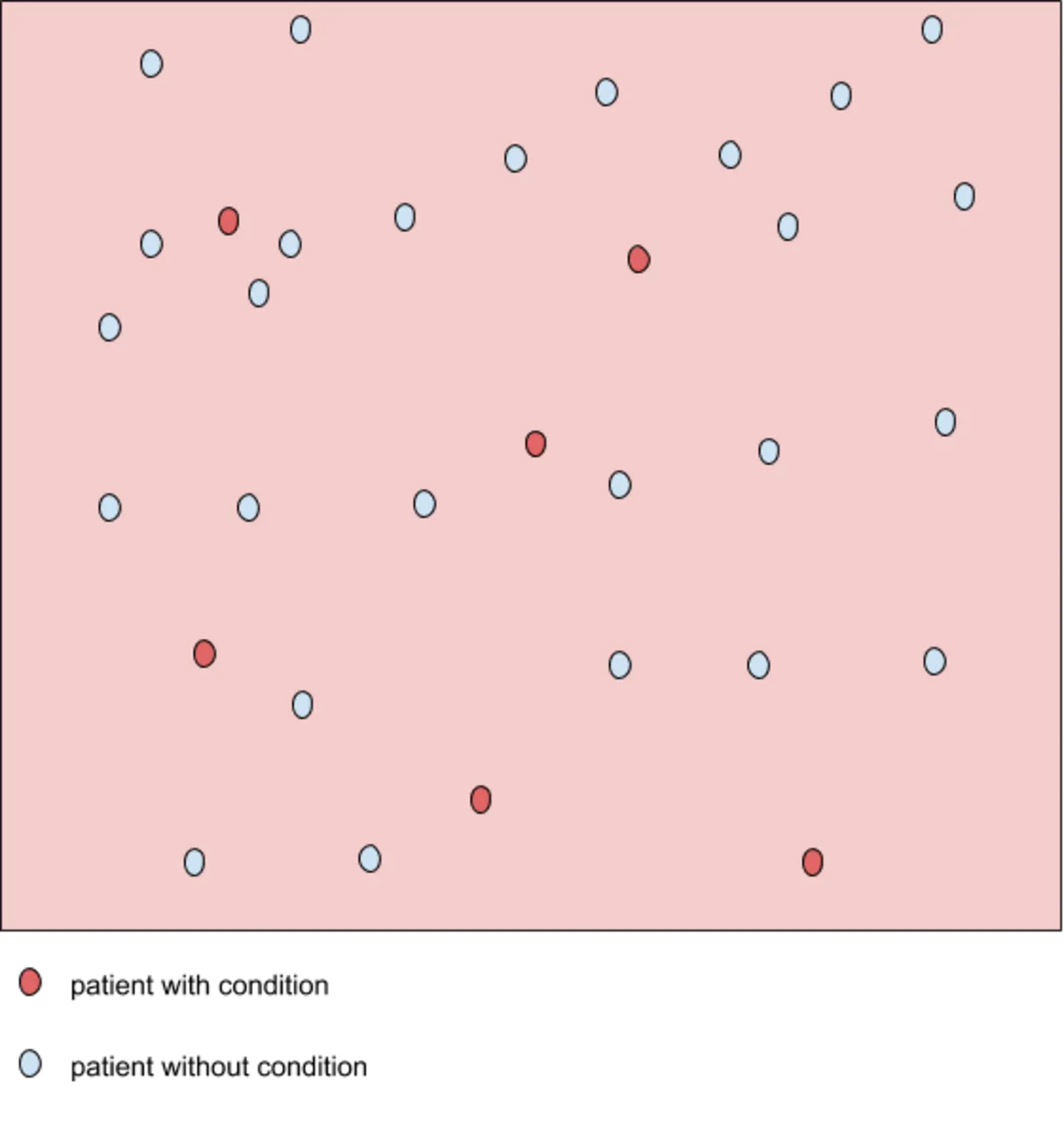
Let's use the image above to buttress the point we have explained above. The above image may look meaningless to a lay man, but it speaks volume in the eyes of the statistician, quality officers etc.
The red dot indicates the patient with the medical condition. The red background indicates the area where the test predicts the data point to be positive. The true positive in this figure is 6, and false negatives of 0 (because all positive condition is correctly predicted as positive), therefore the sensitivity is 100%.
Sensitivity is more focused on true presence of a disease being present and doesn't take into account whether it is absent. If a patient is known to have for example, HIV infection, a screening kit, Point of care testing for example, should he able to detect this virus and read positive, indicative of the viral antigen/antibody presence in the sample.
A medical equipment that cannot sense the presence of even an infinitesimal presence of a measurand cannot be regarded as being sensitive. Though, there are level of sensitivity and this is why, most manufacturers state the degree of accuracy and sensitivity of their equipment. This means that at a concentration, less than the stated one in the manufacture's manual, the possibility of analyte detection is diminished. This is also referred to as the limit of detection (LOD).
On the other hand, specificity is much more concerned with the absence of the analyte of interest. Hence, it is also referred to as true negative (TN). When defining specificity in relation to medical diagnosis, it doesn't take into account the presence of the the analyte, rather it is more concerned with the ability of the testing system to detect that the measurand is not present in the sample. That is to say, the sample is truly negative.
Additional models that are used to explain sensitivity and specificity are False positive (FP) and False negative (FN). In some scenarios, machine interference, methodology, reagents, etc. could have some effects on the outcome of a medical diagnosis and as such altering the expected results.
Cases where the interference leads to a positive result, such case is referred to as false positive while in situations where the interference leads to a negative results, such case is false negative. In this case, the overall results cannot be considered valid.
Very importantly, it is worthy of note that, the two major concepts- sensitivity and specificity have an inverse relationship. The more sensitive a test procedure or devise is, the less specific it is and vice versa. This is the typical settings in the health system. In some cases, sensitivity and specificity are not just enough to fully justify medical diagnostic results. Concepts like accuracy and precision also have huge role to play.
The concept of Accuracy and precision
Note, a machine or device can be precise but not accurate. These two terms are another very important component of quality care. During my training in quality management system early last year, I got to understand the deeper meaning of what it really means when we say a test is precise or accurate.
Precision is independent of accuracy. That means it is possible to be very precise but not very accurate, and it is also possible to be accurate without being precise. The best quality scientific observations are both accurate and precise
Precision is simply the closeness of repeated measurements of a particular sample to one another and how far they are from the correct value of measure (the real value). In precision, the trials or results gotten from the measurements of a sample can be very close to each other but still are not close to the standard value.
Accuracy on the other hand is simply the nearness of a repeated measurement values to a true value or standard.
Assuming you are asked to measure an analyte whose standard concentration has been established to be Xg/mol and upon measurement, your first measurement values read U, V, W, Y, and Z(g/mol). On measuring the analyte again, you got X, X, X, X1 and X (g/mol). Looking at the first measurements, you would observe that the values are closely related and also, they happen to circumvent the true value which is Xg/mol, in this case, we conclude that the equipment used or the measurements is precise.
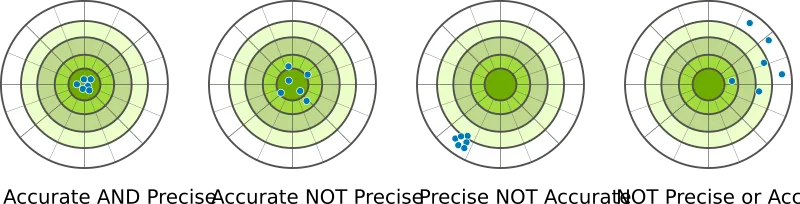
All Possible cases of accuracy and precision
However, with the second measurements made, all the value gotten where close and exactly similar to the true value. In this case, we say the measurement is accurate. Depending on the degree of the precision and accuracy, the measurements can be said to be with high/low accuracy, high/low precision. The images below gives a clearer understanding of the concept.
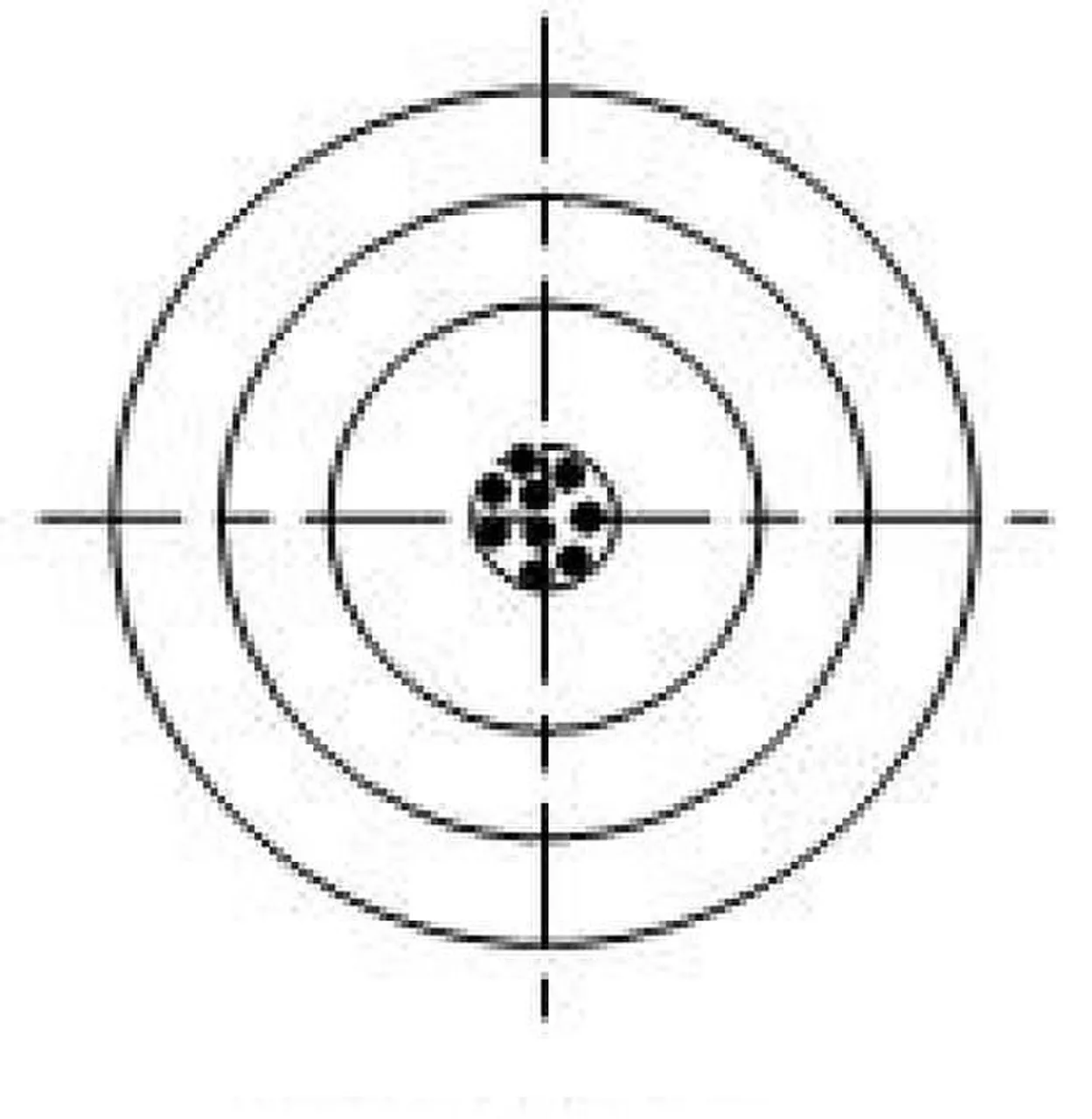
Case of High accuracy and high precision
Looking at the image above, you would observe that all the measurements fell within the central core aka the target zone and in addition, all the different values of measurements gotten are all close. In Such a case, the measurements or equipment used is said to have high precision and accuracy. This is referred to as the best quality scientific observation.
Quick look at the image below shows that most of the measurement values where scattered across the true value while only about two where within the range of true value. This is depicted by the black dots located within the central core of the image. For the fact that the equipment or machine used was able to accurately measure the values that are exactly or close to the true value, , it is accurate.
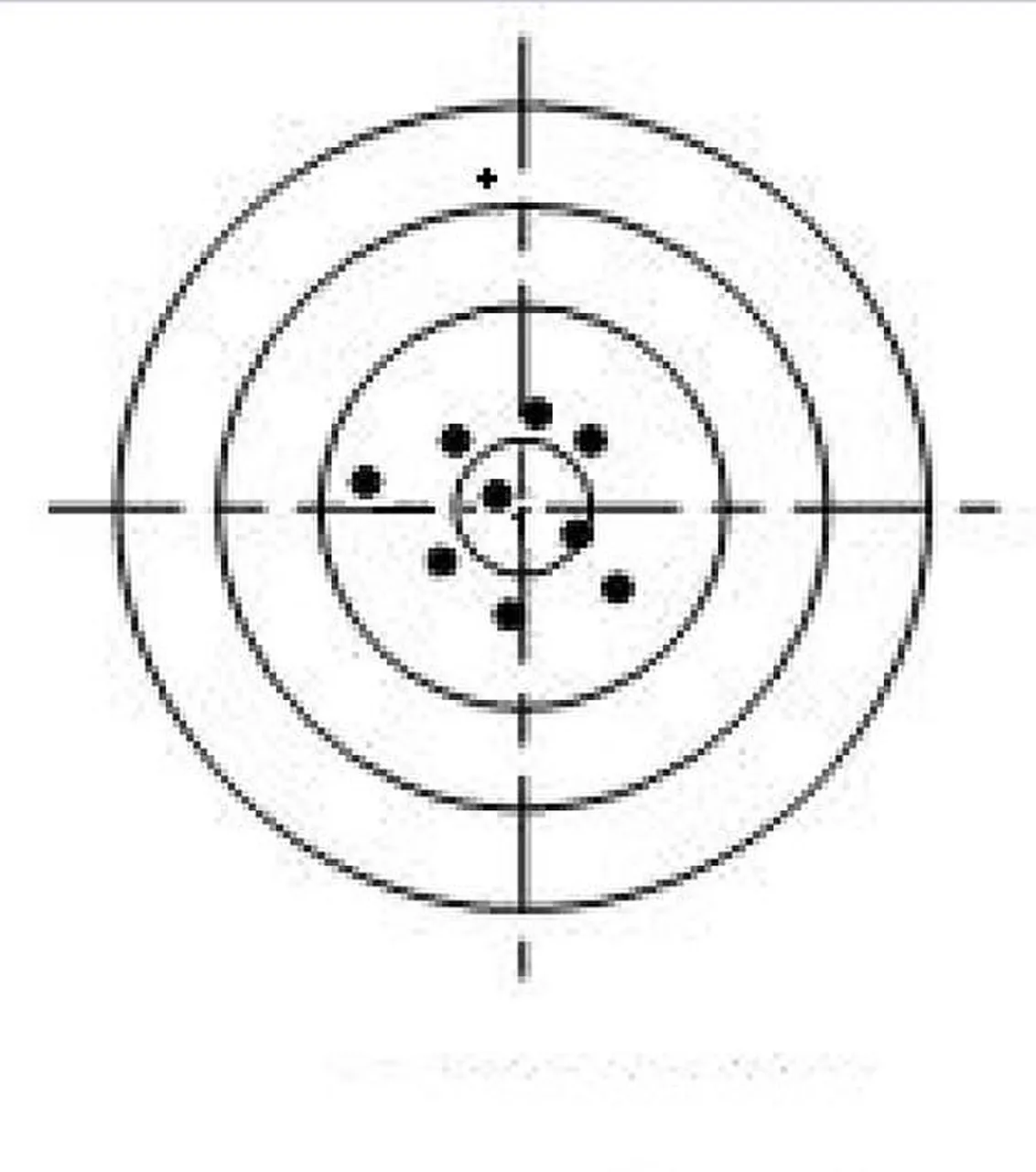
Case of High accuracy and low precision
Reliability and validity of medical equipment
Reliability of a medical equipment is determined by its ability to consistently give accurate results for what is being measured. It is the ability of the instrument to always give accurate results at all times. Validity on the other hand, answers the question, to what extent or degree is the equipment able to give the accurate results.
When an instrument is unable to consistently produce accurate results, then the reliability and validity becomes questionable. The importance of ensuring that equipment used in carrying out diagnosis produces reliable and valid results is of essence. Once we loose confidence in our equipment functionality, then it simply means that the results it produces cannot be relied on.
The use of biomedical equipment has so far formed an integral component of the health care system. These equipment assist and make healthcare delivery faster and more efficient. The need to ensure that they are accurate and producing results that are reliable and valid is very critical in determining good prognostication. Determining their sensitivity by making multiple measurements and checking the pattern of detection by comparing them with known standards, will help boost the trust in the health system.
Imagine using a CT scan, X-ray, ECG, ELISA machines etc. that are not calibrated, it will only end up complicating the patient condition. Most of the results produced by these machines aid and guide the physician and medical professional on the what to do. Wrong results produced if not detected can lead to wrong medical approach to treatment and this is why, having confidence in the functionality, reliability, validity, sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and precision of a medical equipment foster and promote quality health care delivery.
Let's quickly round up with the ear flushing procedure I went for, you might also have one or two things to learn from it.
Ear waxification and flushing
The ear is the human hearing organ that plays other roles besides functioning as sound reception. It also has balance function in humans by virtue of the internal ear structure. Your ability is hear sounds is a function of the entrance of sound waves that hits the tympanic membrane (ear drum).
These sound is then transmitted through the middle ear to the inner ear and to the brain for interpretation. It is not as simple as this anyway, I just want to make the discourse less difficult to comprehend.
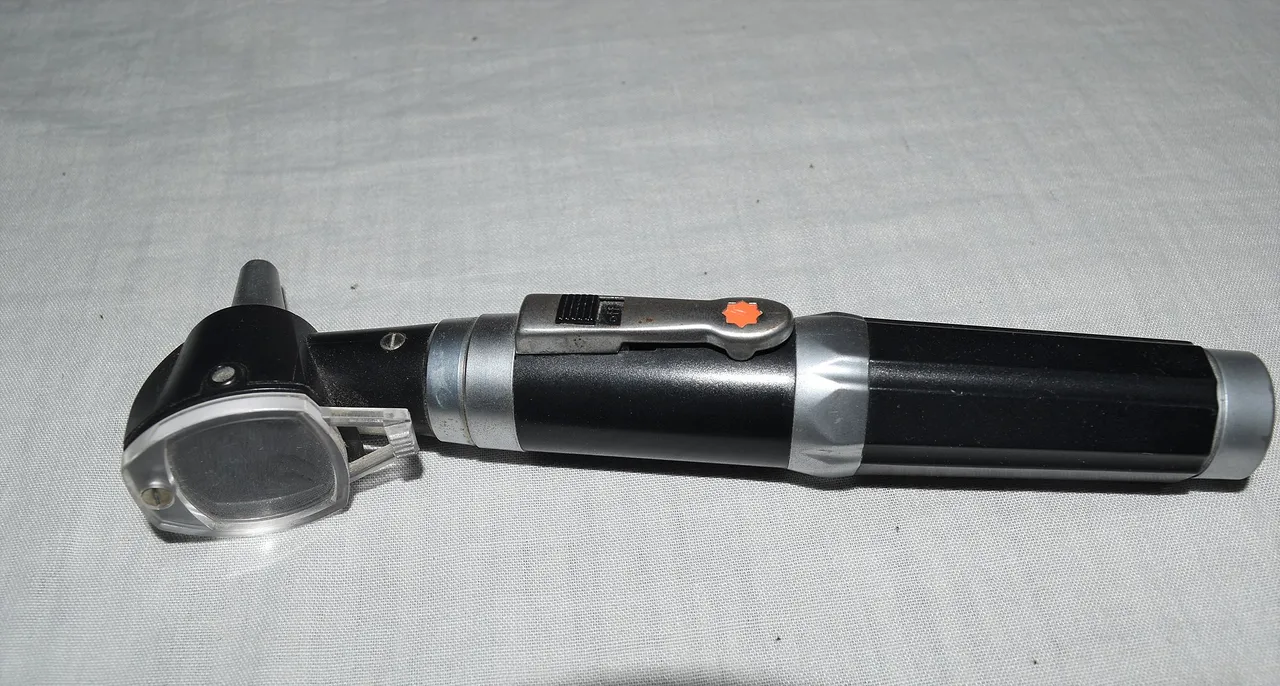

Orthoscope for ear examination
Ear waxification could be caused by over caused by overactivity of the ceruminous gland in the ear. Its hyperactivity causes an increase production of cerumen (ear wax). All things being equal, ear wax is protective in nature because they play the role of naturally cleaning the ear and also protecting it from bacteria infection. The Information below highlights the various functions of the ear wax;
•is a natural moisturizer, preventing the skin inside the ear from becoming too dry
•traps dirt and dust before they can reach deep into the canal
•absorbs dead skin cells and debris
prevents bacteria and other infectious organisms from reaching the inner ear
When this wax is produced in excess, they build up and clog the ear, consequently causing hearing loss and discomfort in the form of a continuous ringing sound. These were practically some of the symptoms I experienced when it happened to me. In case ceruwax (ear drop specially designed to remove and dissolve excess ear wax), is not readily available.
You really don't have to panic, should you experience such, One of crude way of dissolving the ear wax is using olive oil. Adding 3 drops, three times a day into the ear canal and subsequent draining as well helps to soften the wax, after which ear flushing or irrigation is done using normal saline (physiologic water)
As the normal saline is injected into the ear, the reflux pressure of the water coming out of the ear, carries along the softened wax particles out of the ear. This procedure is actually simple and straight forward. I opted for this technique rather because ear irrigation is much more suiting to me than the use surgical tools.
Discomfort associated with ear waxification are usually not painful unless, there is possibility of inflammation in the ear. Preferably go for a medical check up when necessary. The orthoscope will be used to have a glance into your ear. Whatever the case is, with the orthoscope, it will be detected.
Imagine if the orthoscope was not reliable and unable to allow clear visibility of the clogged wax, it would have been more difficult diagnosing the real cause if my discomfort then. Calibration and practice if quality management is very important and must not be overlooked.
Embrace quality Health Care!
Till I come your way, stay awesome.
References
•What is the difference between Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)?
•Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation
•Understanding and using sensitivity, specificity and predictive values
•Practices of Science: Precision vs. Accuracy
•Reliability and Validity
•ISO standard
•How to Determine the Validity and Reliability of an Instrument
•3 reasons to leave earwax alone