This is one research work I really enjoyed getting myself involved in during my internship training in Abuja. A retrospective study findings can be very interesting and it also demonstrates the very importance of biological sample preservation.
One of the commonest things associated with HIV infection is the destruction of immune cells that fight and ward off infectious agents. In an apparently healthy individual, on contact with some potential pathogens, the body system through the white blood cells can comfortably kill and destroy these pathogens but the case is not the same in HIV infected patients.
In HIV patients, the immune system fighting cells are already destroyed by the virus thus, leaving the body of the patient at the mercy of other pathogens. Their body becomes susceptible to harm by some microorganisms that, on a normal day cannot harm the body. These microorganisms that take advantage of immune-compromised or weakened immune systems are generally referred to as opportunistic pathogens and the disease they cause is called opportunistic infections.
let's begin with the brief abstract of the research work.
Abstract
The sole aim of this study is to monitor the level of correlation between the General outpatients department (GOPD) and Special treatment clinic (STC) Patients whose samples (sera and sputa) were tested and confirmed with Western Blot, for HIV-1 and Ziehl Nielsen, Z N Stain/ Lowenstein Jensen, L slope culture for Sputa respectively. These samples were screened for HIV- 1 using three test principles; Determine, Capillus and Genie. Positive samples were confirmed with the Western Blot assay. Sputa samples of the same patients were collected and tested for Mycobacterium spp. infection using the Ziehl Nielsen staining technique and the Lowenstein Jensen Slope cultural technique. The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was 0.466 (P<0.1) showing a relatively high level of concordance between Western Blot confirmed positive HIV-1 infection and Mycobacterium spp. infection in the same patients.
Keywords: Mycobacterium, Ziehl Nielsen Western Blot Lowenstein Jensen Slope.
Introduction
Various reports have shown that the most common pathogen that has so far been found to be usually associated with HIV infection is a bacteria of the Mycobacterium family. Specifically is that of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Mycobacterium spp. the etiologic agent of Mycobacterium tuberculosis disease (TB) has been found associated with HIV-1 infection in several studies along this line of reasoning. Critical assessment of this sort of association is of utmost necessity in this context as a sort of swift clinical intervention for Koch’s disease.
Tuberculosis was popularly known as consumption for a long time before it was later changed to the recent name. Scientists know it as an infection caused by M. tuberculosis in 1882, the microbiologist Robert Koch1: discovered the tubercle bacillus, at a time when one of every seven deaths in Europe was caused by TB.
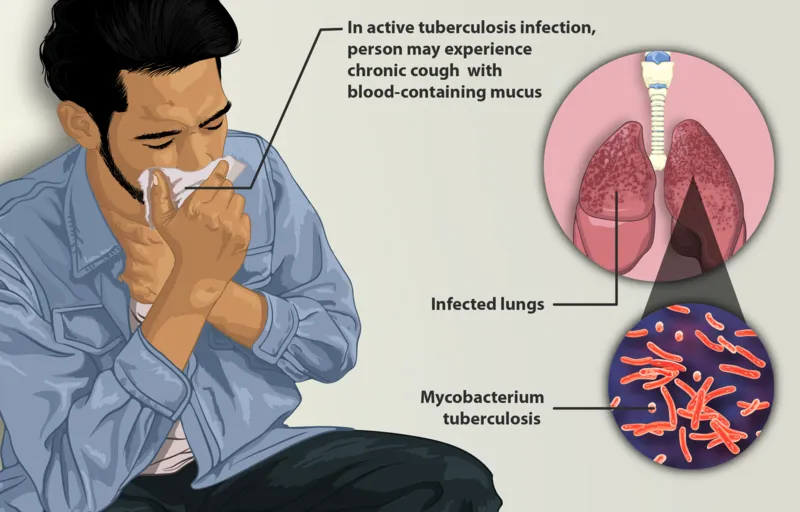
Patient suffering from tuberculosis
Bacteria under the family Mycobacterium are uniquely known for their resistance to normal penetration of stains used for staining other bacteria. Their body wall is naturally shielded with an acid called mycolic acid which is mucoid in nature. They got their name from the word mycolic obviously and mostly dwell where there is a high concentration of mucous, e.g. the respiratory tract. This is one of the reasons they are more abundant in the sputum of patients. They are released when these infected patients cough or sneeze.
Because antibiotics were unknown, the only means of controlling the spread of infection was to isolate patients in private sanatoria or hospitals limited to patients with TB a practice that continues to this day in many countries including Nigeria. The net effect of this pattern of treatment was to separate the study of tuberculosis from mainstream medicine.
Entire organizations were set up to study not only the disease as it affected individual patients but its impact on society as a whole. At the turn of the twentieth century, more than 80% of the population in the United States were infected before age 20, and tuberculosis was the single most common cause of death. By 1938 there were more than 700 TB hospitals in some countries.
Some reports have it that Mycobacterium tuberculosis is usually opportunistic in HIV-1 infection. Screening for HIV- 1 could be done using three test principles; Determine, Capillus and Genie. Positive samples were confirmed with the Western Blot assay. Sputa samples of the same patients were collected and tested for Mycobacterium spp. infection using the Ziehl Nielsen staining technique and the Lowenstein Jensen Slope cultural technique.
Control Samples: (HIV-1 Assay) Control sera, both positive and negative controls as well as the internal controls were supplied by the kit manufacturers and were applied and used as instructed.
Control Samples: (for Mycobacterium spp. Assay) Negative controls were obtained from known and pooled negative sputa of Patients while positive controls were obtained from known and pooled positive sputa of patients using the ZN/LJ Mycobacterium spp. Assays.
Materials and Methodology
I was fortunate to be part of this retrospective study of HIV samples collected from patients for almost two decades now. This is to tell you the power of specimen preservation.
Mycobacterium spp. infection may be associated with HIV-1 infection. Critical assessment of this sort of association is of utmost necessity in this context, as a sort of swift clinical intervention for Koch’s disease: which might be opportunistic in HIV-1 infection.
A total of 211 Patients had their blood samples prospectively collected between January to October 2003: while a total of 443 Patients had their blood samples similarly collected between January to October 2004. These samples were screened for HIV- 1 using three test principles- Determine, Capillus and Genie. Positive samples were confirmed with the Western Blot assay.
Sputa samples of the same patients were collected and tested for Mycobacterium spp. infection using the Ziehl Nielsen staining technique and the Lowenstein Jensen Slope cultural technique. A total of 211 Patients had their blood samples prospectively collected between January to October 2003: while a total of 443 Patients had their blood samples similarly collected between January to October 2004.
These samples were screened for HIV- 1 using three test principles- Determine, Capillus and Genie. Positive samples were confirmed with the Western Blot assay. Sputa samples of the same patients were collected and tested for Mycobacterium spp. infection using the Ziehl Nielsen staining technique and the Lowenstein Jensen Slope cultural technique. The total duration of the work was 20 months.
Test principles - (HlV-1 Screening assays)
Determine: Determine HIV-1/2 is an immune chromatographic test for the qualitative detection of antibodies to HIV-1 and HIV-2. The blood plasma or serum sample of the patient is added to the sample pad. As the sample migrates through the conjugate pad, it reconstitutes and mixes with the selenium colloid-antigen conjugate. This mixture continues to migrate through the solid phase to the immobilized recombinant antigens and synthetic peptides at the patient’s window site.
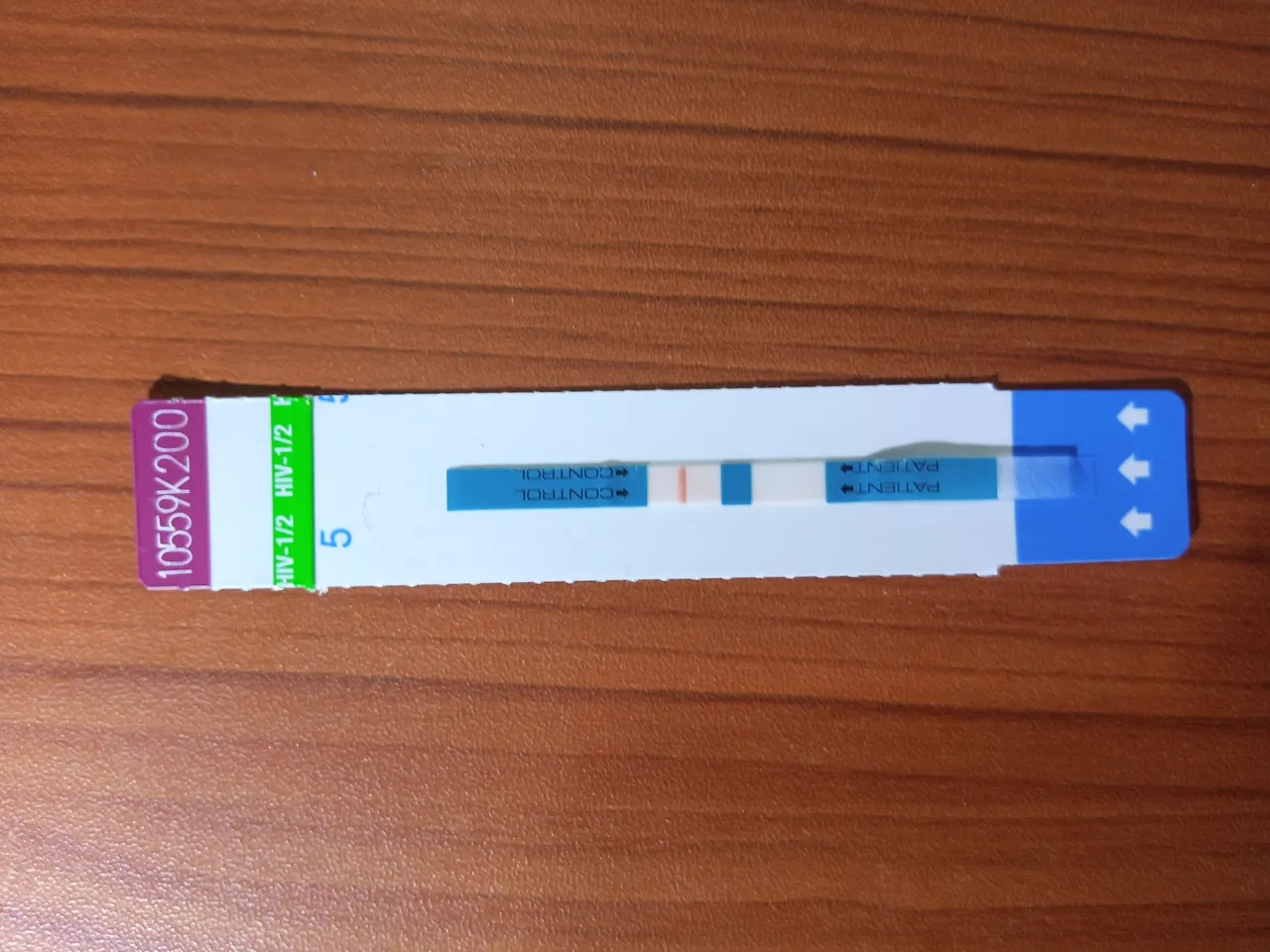
Negative test result for HIV using Determine kit. Image by @cyprianj
If antibodies to HIV-1 and/or HIV-2 are present in the sample, the antibodies bind to the antigen — selenium colloid at the patient window, forming a red line at the patient’s site. If antibodies to HIV-l and/or HIV-2 are absent, the antigen selenium colloid flows past the patient window and no red lines are formed at the patient’s window site. To ensure assay validity, the procedural control bar is incorporated into the assay device.
For a detailed explanation of the principle of lateral flow kits, kindly read this post - are pregnancy test strips good enough to confirm pregnancy status, you will have a better understanding of the concept.
Cappillus Assay
The majority of antigens from the envelope proteins of HIV-1 and HIV-2 have been identified and cloned using recombinant DNA technology. These HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteins have been expressed and purified. The Trinity Biotech Capillus, HIV- I, and HIV-2 employs these two proteins bound to polystyrene latex beads to form the basis of a direct latex aggregation assay for the detection of antibodies to HIV-I and HIV-
2 in the human serum, whole blood, and plasma. The assay is performed on a patented capillary slide.
Genie Assay
The (Gennie II HIV-1/HIV-2 is a dual recognition enzyme — immunoassay (EIA), based upon the specific detection of antibodies HIV-1 and HIV-2 antibodies by antigens that bind both antibody binding sites. The test incorporates a combination of immune - chromatography, and immuno-concentration.
The reaction device contains two ports, a circular specimen Port A for the addition of specimen: and a larger elliptical reaction Port B. Antigens derived from HIV-I and HIV-2 are immobilized in two separate spots on the reaction zone of port B. A third spot serves as the internal control for monitoring the performance of the test. The procedure followed was as given by BlORAD 3 Boulevard Raymond Poincare: 92430 MARNES COQUETTE-FRANCE.
Western blot confirmation assay
(New-Lav Blot-1) Principle: The test is based on the indirect ELISA technique on a nitrocellulose strip containing all the HIV — I constituent proteins and internal anti IgG control. The band corresponding to the internal control is localized on the strip end without any number, before the P-18 reaction and allows validation of the addition of the sample and reagents as well as the correct progress of the procedure.
Inactivated HIV- 1 proteins are separated according to their molecular weights by polyacrylamide gel electrically transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane sheet.
Reagents are first stabilized at room temperature for 30 mm. Strip is dehydrated by adding 2m1 of the reconstituted buffer solution into each cell for 5mm. 2Oul of each sample or control serum is added to the corresponding cell for 2hrs incubation and continuous slow shaking. The contents of each cell are completely drained using a vacuum pump.
Each strip is washed 3times with the reconstituted buffer. 2m1 of the conjugate is dispensed into each cell and then incubated for 1hr at room temperature. They were washed as stated above. 2m1 of color development solution was dispensed into each cell for 5mm incubation at room temperature under slow shaking.
The reaction is stopped by removing the development solution and rinsing the strips three times with distilled water. Strips are dried between 2 sheets of absorbent paper at room temperature. The bands on the trips are then validated and interpreted according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Ziehl- Nielsen staining Procedure
The reagents used were Carbol fuchsin: a saturated solution of basic fuchsin (3g of basic fuchsin in 100ml of 95% ethyl alcohol), 5% aqueous solution of phenol, 3% acid alcohol, 0.3% aqueous; the detailed procedure was followed.
A smear (1cm x 2cm) was prepared on a labeled, grease-free slide. The slide was placed on a hot plate at 85°C for 15 mins. in a p.3 safety cabinet. The smear was flooded with Carbol fuchsin and was allowed to stand for 15mins at room temperature.
It was steamed gently with a flame from the underside for some minutes (but it wasn’t allowed to boil). The stain was allowed to stand for 5minute on the slide and then washed with distilled water and tilted to drain. The stained slide was completely decolorized with 3% acid alcohol.
The slide was rinsed with distilled water and tilted to drain. The slide was flooded with methylene blue for one minute. The slide was rinsed and allowed to air dry. The slide was then examined under an X100 oil immersion lens.
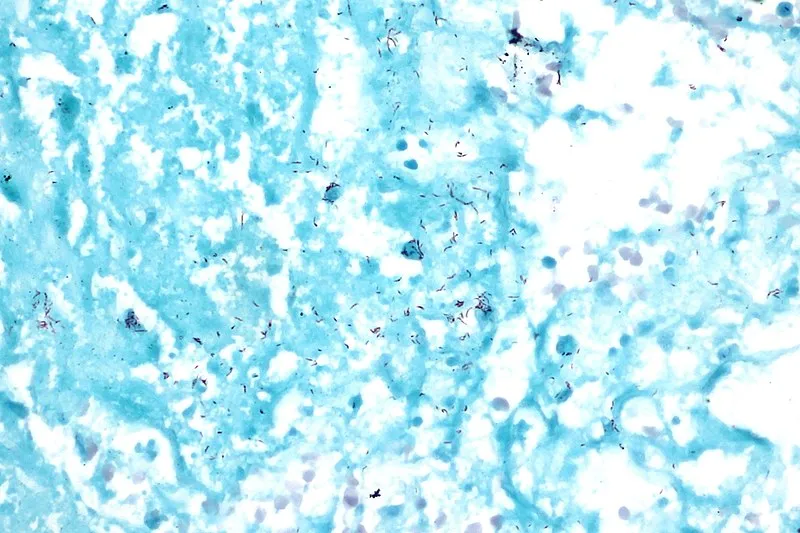
Acid fast Ziehl Neelsen stain of the bacilli - Mycobacterium tuberculosis; How they appear under the microscope. The spiral-shaped tiny rods are the bacteria that causes tuberculosis in humans. They are usually coloured pink
As a side note here, while using the X100 oil immersion lens to view stained slides, ensure you open the condenser aperture of the microscope in order to allow sufficient light to pass through the slide.
Results:
Table 1: Table of total patients confirmed positive for Both Western Blot and Ziel Nelson assay in the years 2003 and 2004, from January to October.
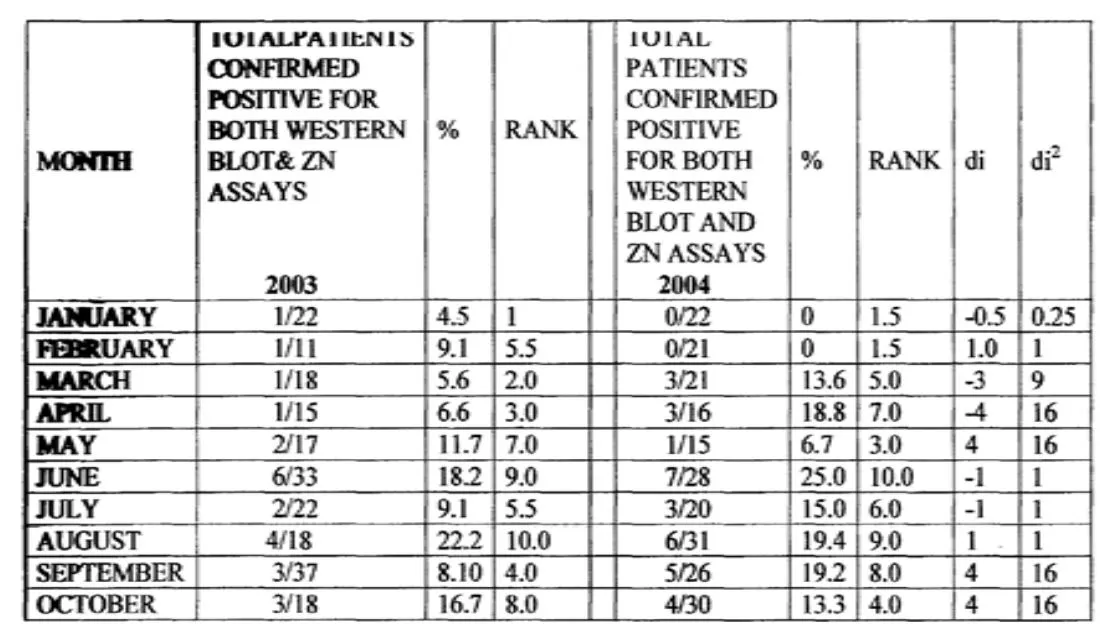
There seems to be a remarkable increase in the number of patients confirmed HIV positive in June for both years. Judging from the climatic condition then; which happens to be the rainy season in Nigeria, the spike in both years could be a result of an increase in sexual activities among individuals, since such weather favors sexual acts unlike in the early beginning of each year that recorded low values up until mid-year.
Table 2: Showing total positive and negative results for both Western Blot and Zeihl Neelsen staining assays for both 2003 and 2004 years.
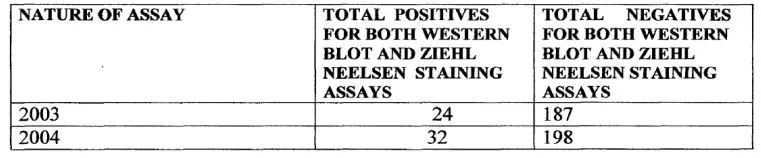
The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was 0.466 (P<0.1) showing a relatively high level of concordance between Western Blot confirmed positive HIV-1 infection and Mycobacterium spp. infection in the same patients. This simply implies a strong correlation and also shows that most HIV patients are highly susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Conclusion
Mycobacterium spp. which may be reliably tested in Sputa samples of HI V-I positive patients using the above techniques-appears to be a strong indicator of opportunistic infection in HIV- I infected patients. It is suggested that early diagnosis of this, will enhance treatment response in HIV patients under retroviral drug therapy.
In addition, it is advised that mycobacterium spp. assays are incorporated in the treatment and management of HIV patients. Screening for the presence or absence of this bacteria will properly guide the physician.
The article was published in open access journal, so feel free to access the original article through my research gate profile here. But the read here is quite more comprehensible. Click the 'more' icon if you choose to download the article to read at your convenience.
Until I come your way, stay awesome.
References
1. McGraw, H. (2002). Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine @ 2002 by McGraw Hill
2. Ushananthini, A. S. (2012). Assessment of DNA Damage in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients by Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis/Comet Assay (Doctoral dissertation, Swamy Vivekanandha College of Pharmacy, Tiruchengode).
3. Koch, R. (1881). "Zur Ätiologie des Milzbrandes" On the etiology of anthrax]. Mittheilungen aus dem Kaiserlichen Gesundheitsamte. (2010). Berlin: Robert Koch-Institut, 174 206
4. Abott, L. (2000). ABOTT Laboratories Diagnostic Division SEPT.2000, 100, Abott Park IL60064 USA
5. Trinity Biotech; Trinity Biotech 2005 www.Trinitybiotech.com
6. Bio, R. (2000). Biorad 3 Boulevard Raymond Pointcare 92430 MARNES COQUETTE FRANCE.
7. Monica, C. (2001). Regional or Central Microbiology Laboratory for pathogen identification. The 3rd edition, 2001; Principles of Medicine in Africa.3. 462 pages
8. Tuberculosis
9. TB and HIV Coinfection