Hi Everyone,

The application of economics has been around since people first started interacting with each other. However, it was not until much later that economics was recognised as a social science. It was after Adam Smith published his book ‘An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations’ that economics became widely recognised as a field of study. Over the years, the field of economics has expanded. It now covers a wide range of areas at both the macro and micro levels as well areas that fit in-between. Economics frequently borrows, works with and integrates with many other fields in both social science and science.
One of the most significant additions to the field of economics is behavioural economics. Behavioural economics focuses on why people make particular decisions. Aspects of behavioural economics have inspired several of my posts. Below are a few examples of such posts.
- Reflecting on Past Decisions
- Time to Play the Game
- Making the Most of Our Time
- Quality of Life as Quality of Time
- Social Economic Utility Analysis (working title) Model
- How often do you want to succeed?
- What do we want?
- Power, Money and Me Me Me
Another great addition to economics is game theory. Game theory belongs to the field of mathematics but is so frequently integrated into economic thought and theory that it can be considered as part of economics. I have discussed game theory several times in my posts. You can read/watch all of my content relating to game theory in my Collection of Works (Part 1). The extent of the potential application of game theory is very wide.
Freedom Based Economics

In this post, I want to discuss another possible addition to the economics family. For now, let us call it Freedom Based Economics. Many of the ideas I want to express build on existing theories such as behavioural economics and game theory. Elements of it may bear some resemblance to libertarianism but it is economic rather than political in nature. Freedom Based Economics is about understanding how freedom affects the quality of life of all. Freedom creates opportunities for people to live their life in a manner they most desire.
Freedom Based Economics will have a strong focus on usage of time and the quality of that usage. Time can be used in many ways. It could be used to earn an income, it could be used for enjoyment, or it could be used for both at the same time. If we have more freedom to determine the usage of our time, we can improve the quality of our lives.
What do I mean by Freedom?

Freedom is to possess the opportunity to make decisions based on your own beliefs and desires. Any form of constraint reduces that freedom; these could be physical, psychological, legal, religious, or cultural constraints.
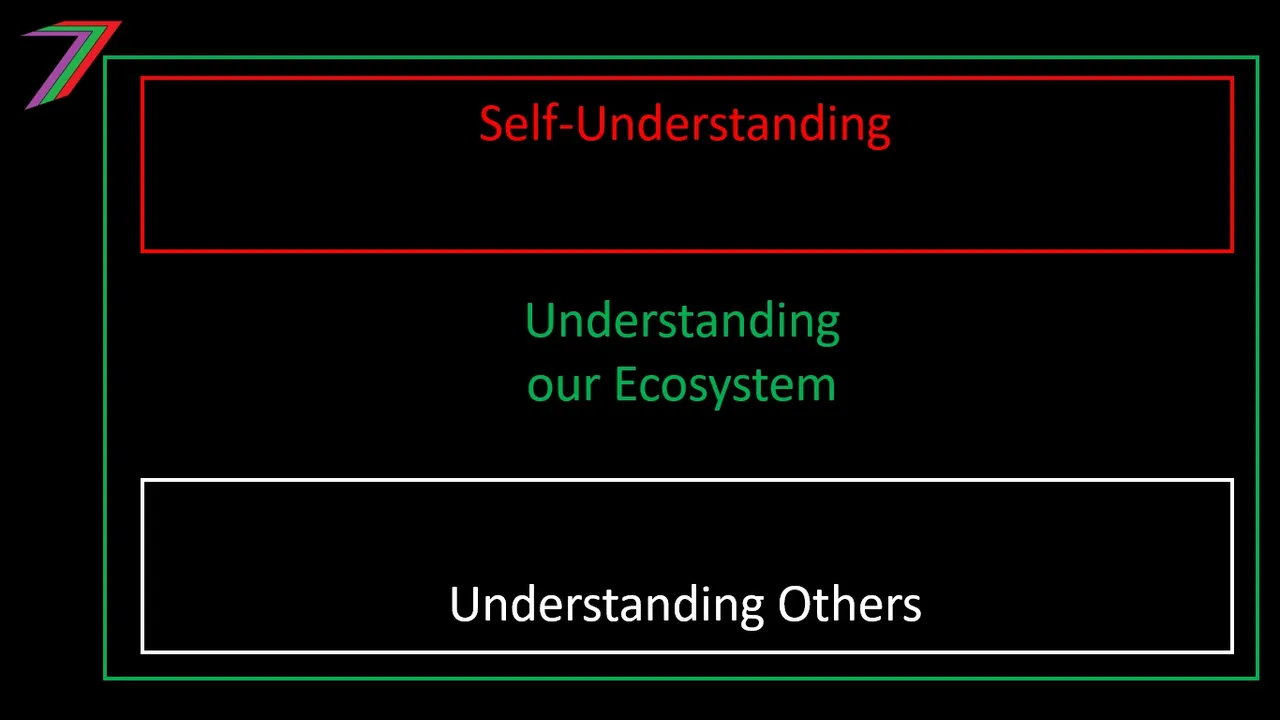
Obtaining, maintaining, and expanding our own freedom does not occur automatically. It requires active pursuit. I have outlined several steps that may increase freedom and access to freedom. This is a preliminary list to demonstrate that steps are necessary to facilitate freedom. The steps I describe are as follows:
- Self-understanding
- Understanding our ecosystem
- Understanding those within our ecosystem
- Competition and cooperation
- Innovation and improvement
Self-understanding

A fundamental step to achieving freedom is being able to understand one’s self. If people do not understand themselves, they will not be able to understand fully what they believe, need or want; hence, have limited freedom. The task of self-understanding is not likely to be simple. We are exposed to and therefore potentially influenced by many different factors. Parents, media, culture, friends, teachers, employers, religion, and potentially many more other stimulants influence our perception of the world. To complicate things further, we could also argue that our genetics are also a determining factor.
For many of us, reflecting objectively on what shapes our personality, perceptions, desires, and motivations is likely to be challenging. People’s process for reflection is tainted, as it is guided by their own perspective. Another problem people face is that they constantly encounter new forms of influence or stimulus. Therefore, people are likely to be constantly changing. This means that self-understanding is a continuous journey rather than a one-off self-assessment. A person could request the help of a third party to explore how they are influenced but a third party is limited by incomplete information about us as well as restricted by their own perception.
Despite the challenges, an attempt to self-understand can be made. People can learn to understand better what and how things influence and affect them through their own experiences and/or with the help of others. A greater problem is likely to be an unwillingness to admit effort is required to understand one’s self. People may believe that their current attitudes, thought processes, ideology, etc. unquestionably reflect themselves. This state of mind is likely to cause people to pursue goals and objectives that do truly reflect what they believe or want in life. Hence, they do not truly exercise their freedom.
Understanding our Ecosystem

An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system (Wikipedia 2021). We are all part of an ecosystem and we are all connected through that ecosystem. A key step to achieving freedom is understanding our relationship with our ecosystem. Our actions affect our ecosystem as well as others within our ecosystem. Some of our actions may benefit our ecosystem, while others may harm it. The benefit and harm we cause could spill over to other people who share our ecosystem. Likewise, the benefit and harm other people cause could spill over and affect us. Ideally, people will pursue their goals and objectives whilst creating a net benefit to their ecosystem. This is only possible if people understand the importance and relevance of their ecosystem and their connection to it.
Our ecosystem extends beyond just other people. It includes other species as well as the environment. Freedom is also an essential determinant of quality of life for many other species of animals. Many of our choices will greatly affect the quality of life of animals. For industries such as food, entertainment, pets, and clothing our choices directly affect the freedom and quality of life of animals. The environment is essential to all living creatures existing in an ecosystem, as it is needed to support life. A damaged environment can greatly reduce freedom and quality of life. Pollution can obstruct freedom of movement for people and other animals.
Our ecosystem provides both opportunities and threats. We can enjoy our ecosystem by exploring and immersing ourselves in it. It can provide adventure, beauty, and pleasure. However, it can also be dangerous. It is important to understand the potential threats as well as how to be prepared for them if encountered. Knowledge and understanding of our ecosystem is an important step to enable us to enjoy it freely.
Understanding those within our ecosystem
Everyone is different. With some people, we may share many similarities and only a few differences. With other people, we may share very few similarities and have a vast number of differences. Just as we are influenced by many factors in our lives, so are other people. Many of these factors are different and even similar factors may affect different people in different ways. Understanding that different people experience and perceive the world differently from ourselves is important in achieving our freedom as well as not obstructing other people from obtaining their freedom. Building mutual respect amongst people will increase the likelihood of support for each other’s freedom.
Not everyone places great concern for other people’s freedom. Some people may prioritise wealth, power, and pleasure with little regard to how their behaviour may negatively affect those around them. As the number of people with the above-described types of perceptions increases, the level of freedom of society in general decreases. Eventually, if this attitude becomes prevalent, we can expect those who have little regard for other people’s freedom to have their own freedom limited. We can hope a more empathetic and sympathetic society will develop, if people make an effort to understand themselves, their ecosystem and the people who share this ecosystem. However, we should not assume that all societies would naturally develop in this manner.
Competition and cooperation
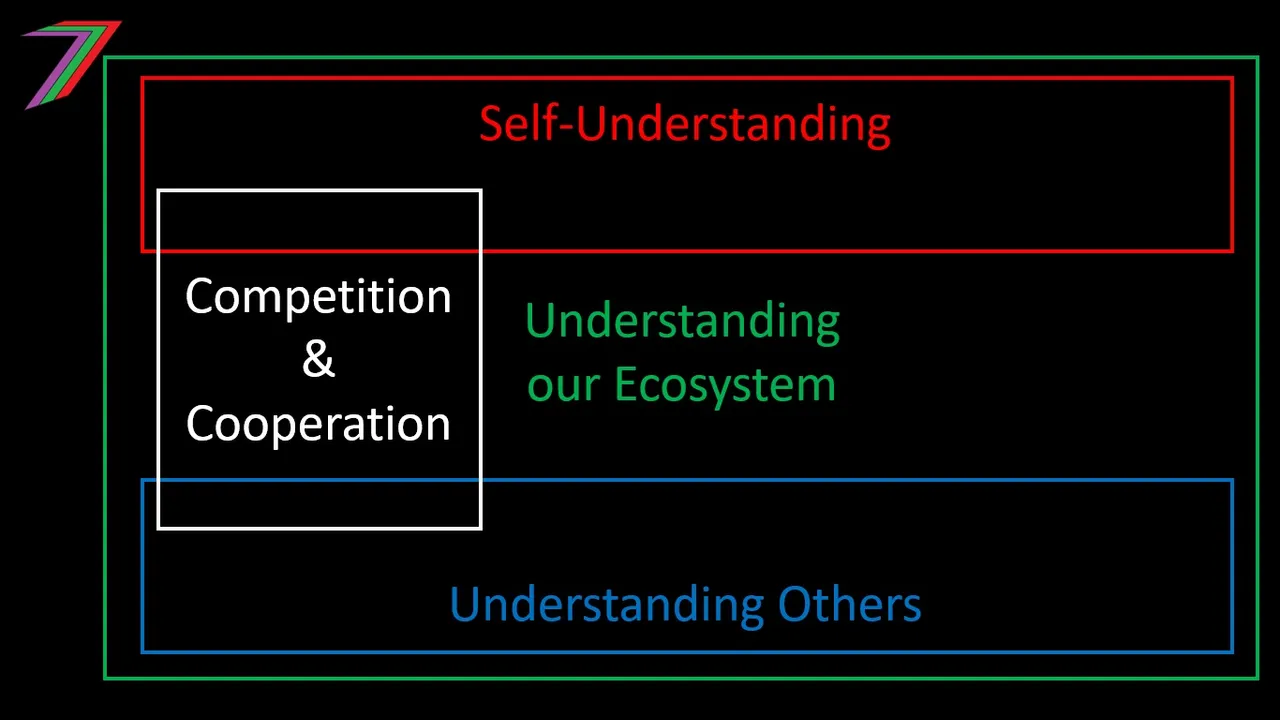
Both competition and cooperation are necessary for people to achieve their goals and objectives. Competition is necessary to obtain or achieve something that is scarce. Scarcity can come in many forms. It can be natural or contrived. Natural scarcity occurs when there is not enough of something for everyone. Therefore, competition is required to determine who obtains the scarce resource. Contrived scarcity occurs when there is sufficient quantity but the supply is being controlled. Those not controlling the supply are required to compete.
Competition can exist for both needs and wants. Competition over needs is a form of survival of the fittest. People most capable of meeting their needs under the prevailing circumstances will be more likely to survive. This is advantageous to the human species, as the people most suited to the ecosystem survive. They are able to pass on their survival traits to the next generation through their genetics or through sharing of skills and knowledge. People, as a species, should strive to exist beyond competing for mere survival or basic needs. Instead, they should compete over wants and ambitions. Under these circumstances, those that do not achieve success are able to learn to increase their chances of success in future attempts.
Cooperation can be used to increase competiveness or decrease the need for competition by reducing scarcity. Cooperation enables a group of people or businesses to compete in many ways. These include shared expertise and knowledge, shared innovations, shared resources, specialisation of skills, and economies of scale. Cooperation can enable a reduction of competition for basic needs. Cooperation can reduce scarcity of resources by improving distribution and availability of basic needs to all people. Cooperation can play a huge role in ensuring that people are able to meet their basic needs.
Innovation and improvement
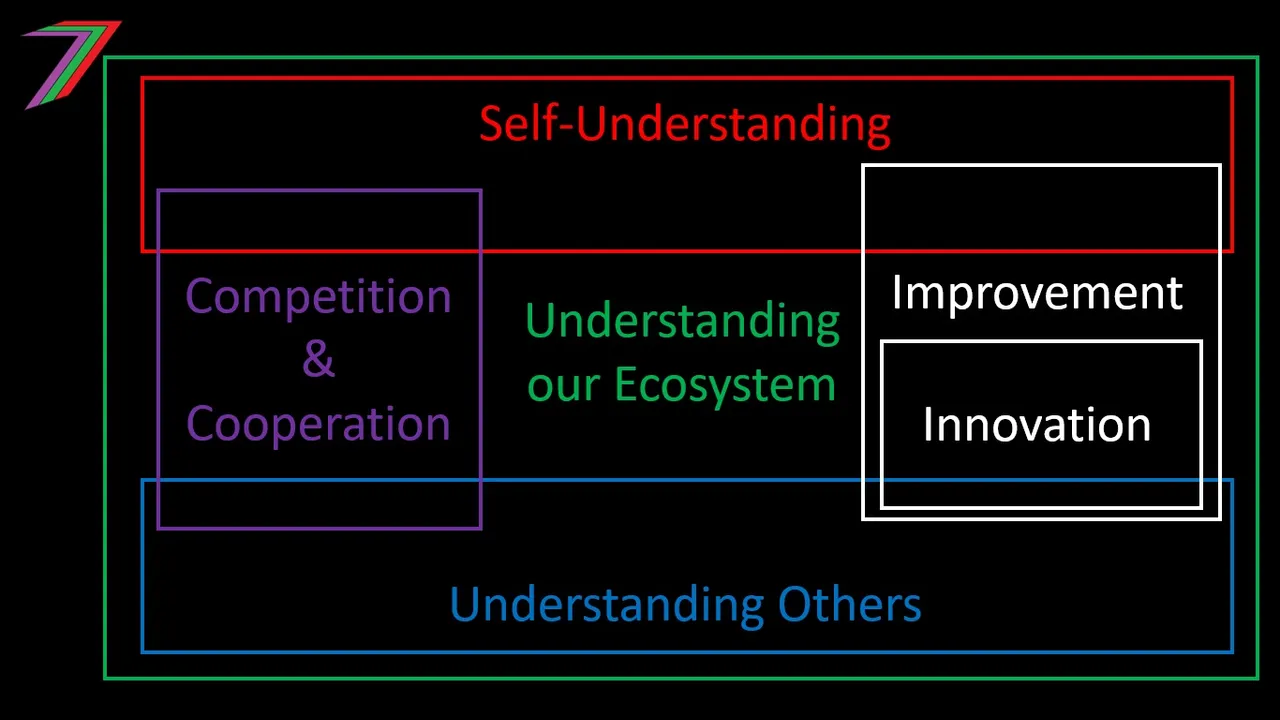
Innovations and improvements can enable people to meet their own needs and wants more easily. Innovation involves developing and discovering new methods or new applications of existing methods. Improvement involves making something better without necessarily employing new ideas.
Innovation can enable greater efficiency and improved outputs. People can spend less time obtaining what they want and more time enjoying it. For example, a person could invent a machine that enables a person to do their job 10 times faster. This person could produce twice the output while working just 1/5th the time (i.e. more freedom to pursue activities outside of work). Innovation can lead to new ways of enjoying life. For example, virtual reality can enable people to virtually visit places and do things that are not possible or too costly to do in real life.
Improvement can come in many forms. Self-improvement is one of the most fundamental forms of improvement we can experience. Self-improvement can be attained through life experiences, learning from others, or from education. Improvement can also come in the form of what people can provide to others or their ecosystem. For example, a person or business could improve the quality and durability of a product. This is good for the person who acquires the product as they will have a better experience and will not require replacements or repairs as frequently. It is good for the ecosystem (e.g. environment) as there is less wastage from less frequent disposal of the product upon failure.
How does it all fit together?

We all face opportunities and barriers to achieving freedom. I believe these opportunities and barriers can be broadly categorised under three areas. These are ourselves, our ecosystem, and other people. We can provide ourselves with more freedom through self-understanding; this will enable us to understand what we need to improve the quality of our lives. We can provide ourselves with more freedom by understanding how we can interact with our ecosystem. We can provide ourselves with more freedom by understanding other people and their possible motivations.
As we achieve a greater understanding, we are able to take actions that can utilise our understanding to achieve more freedom. We can learn how to more successfully compete or cooperate with others to obtain what we want. We can develop new methods of doing things or invent new things to do.
We can expect there to be limits to freedom

It is important to understand that some people will not value the freedom of others. Therefore, complete freedom for all is unlikely to be ever possible. Society will impose restrictions on actions that negatively affect the freedom of others. For example, theft would be considered as an impingement on people’s freedom to possess their own property; therefore, people would not be granted freedom to steal other people’s property. Freedom will be restricted in some way. An optimal level of imposed restrictions needs to be determined so that the net negative effect on freedom is minimised.
How do we measure freedom?
Whenever we advocate for something there is an expectation for some form of measurement. If something cannot be measured, how do we know it exists? We would argue that the extent of freedom is impossible to measure directly. However, we can measure some of the indicators of freedom. For example:
- The number and extent of freedom restricting laws can be measured.
- The number of violent crimes.
- The extent of control of information (i.e. media and social media)
- The application of democratic processes (e.g. elections, referendums, direct public input and consultation).
- The extent of centralisation of control, power, authority, distribution, and production (e.g. Lerner Index).
- Access to freedom of speech (e.g. ability to protest and application of censorship)
- Distribution of wealth (e.g. Gini Index).
- The number of people living in poverty.
- The extent of free movement of people (e.g. travel requirements and restrictions).
A combination of the mentioned indicators of freedom can be used to present a general idea of the extent of freedom a society possesses. However, this will still be incomplete, as some aspects of freedom cannot be easily externalised. For example, the extent of self-understanding cannot be assigned a meaningful empirical value.
Human freedom indices currently exist. One such index is the ‘World Liberty Index’. This index ranks over 100 countries based on an assessment of social and economic freedom using similar indicators to the ones listed in this section.
My work so far

In this post, I introduced the terminology ‘Freedom Based Economics’. In several of my previous posts, I have discussed aspects of the ideas I have presented as part of ‘Freedom Based Economics’. In my post When Less is More, I discuss the possible paradox of freedom. In my post Free movement of people, I discuss migration. In my post Relative Utility Approach, I discuss understanding relative value we obtain from various activities. In my posts Technology – Curse or blessing? and Less jobs vs less working hours – Further discussion about efficiency and technology, I discuss how technology can reduce workloads and improve quality of life. Several of the posts, which I list in the first section of this post also relate to several ideas I have discussed.
More posts

If you want to read any of my other posts, you can click on the links below. These links will lead you to posts containing my collection of works. These 'Collection of Works' posts have been updated to contain links to the Hive versions of my posts.
My New CBA Udemy Course
The course contains over 10 hours of video, over 60 downloadable resources, over 40 multiple-choice questions, 2 sample case studies, 1 practice CBA, life time access and a certificate on completion. The course is priced at the Tier 1 price of £20. I believe it is frequently available at half-price.
Future of Social Media