Crocodiles, the ultimate, primordial predators!
Introduction
If you find Crocodiles as fascinating as I do, you will love this post on these creatures of grandeur.
What are Crocodiles?
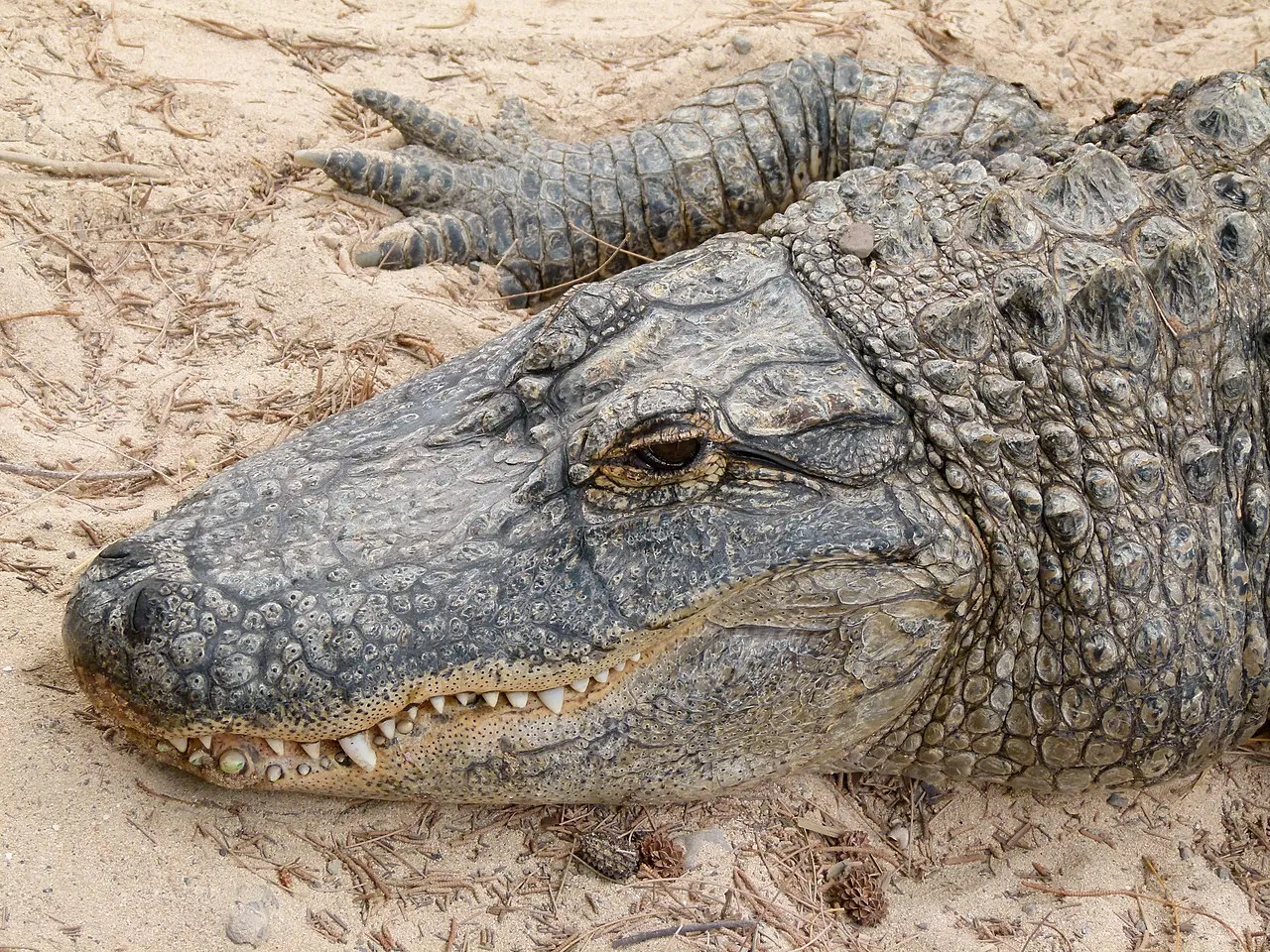
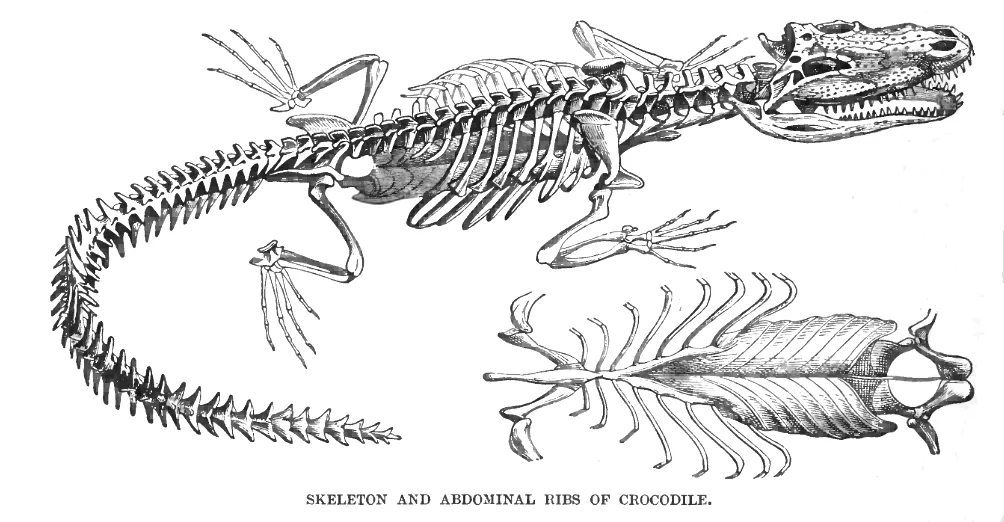
Crocodiles are a type of reptile, meaning they, lay eggs, have cold blood, and are covered in scales.
They have sharp, pointy teeth, short legs, and thick skin that is covered with bony plates.
Some crocodile fossils date back to 200 million years ago, revealing that they are the closest descendants of the dinosaurs.
They are the largest reptiles found today, with some weighing over a ton.
Classification/taxonomy
• Kingdom: Animalia
• Phylum: Chordata
• Class: Reptilia
• Order: Crocodylia
• Family: Crocodylidae
• Genera: Crocodylus, Mecistops and Osteolaemus
Differences Between Alligators and Crocodiles
Crocodiles can be distinguished from their alligator relatives by their narrow snout. They also sport a toothy grin, whereby, its 4th bottom tooth pokes up above its top lip. Their upper and lower jaws are the same width, that look like the letter 'U,' causing their teeth to show when their jaws are shut, whilst Alligators, have a wider upper jaw, that look like the letter 'V, which allows the lower teeth to fall into place, hidden from view.
Also, crocodiles have salt glands on their tongues, that help them to tolerate living in salt water, whilst Alligators and caimans have lost the ability to secrete excess salt through the salivary glands and therefore, find it preferable to live in freshwater areas.
Habitat
All crocodiles are semi-aquatic and dwell in swamps, rivers, oceans, near lakes and even some saltwater regions and can be found in tropical habitats of Africa, Asia, Australia and America.
Adaptations
Crocodiles have special characteristics that enable their survival in their natural habitat.
Crocodiles live in tropical climates because they are cold-blooded, thereby cannot generate their own heat. During colder months or during long periods of drought, they dig out a burrow in the side of river bank or lake, to create a place to settle in for hibernation purposes.
Crocodiles can often be seen basking in the sun on river banks, which serves to warm them after a cool night. This behavioural adaptation is called gaping, which assists them in regulating their body temperature. Reptiles are ectothermic, which means that they use ambient heat to regulate their body temperature.
The adaptation that lets a crocodile eat any animal in its entirety, is the very strong acid in its stomach, which can break down everything it devours.
To adapt to not being able to chew, a crocodile spins its body around with tremendous strength and speed, which helps tear up the food in its mouth.
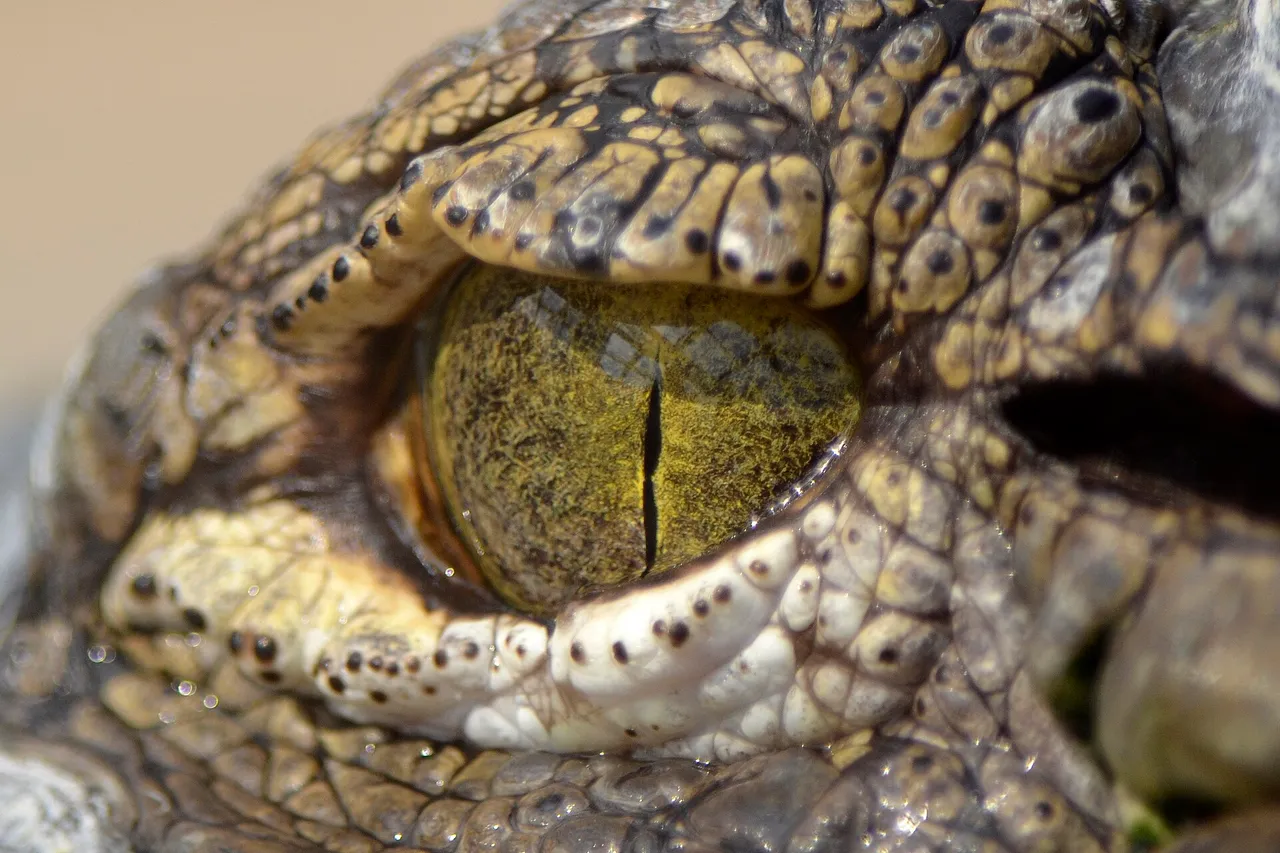
How incredible is this adaptation for the ultimate predator, whereas a crocodiles eyes, nose and ears, sit on top of its head enabling to see and hear whilst under water!
Life Cycle
Crocodiles are naturally aggressive predators, however they nurture and care for their young, before and after their birth. Approximately two months after mating, a female crocodile lays her eggs in a hole that she digs along a riverbed or the shoreline; a process called nesting. She closely guards the eggs and the male stays nearby to protect both the female and their eggs from predators.
Crocodiles generally lay 10 to 60 eggs, at a time, however the number of eggs the crocodile lays varies on the species. Eg. The Nile crocodile deposits anywhere between 25 and 80 eggs, the saltwater crocodile lays 40-60 eggs, and the American crocodile 30-70 eggs, at a time.
The hatchlings stay in their eggs for a period of 55 to 110 days. They are 7 - 12 inches, long when they are born and only mature when they are between 4 to 15 years.
A crocodiles lifespan varies among species, i.e between 30 to 75 years.
example:
the American Crocodile average lifespan is up to 70 years.
the Nile Crocodile lifespan is up to 45 years.
the Saltwater Crocodile lifespan is up to 70 years.
Other facts
• A crocodiles replaces lost teeth very quickly and can go through 8,000 teeth over its lifetime.
• A crocodile does not sweat as they keep cool through a process called gaping.
• Crocodiles do produce tears. They have lachrymal glands, which secretes a fluid behind their third eyelid, which is called a nictitating membrane. This fluid helps clean, lubricate and reduce bacteria in their eyes.
• The jaws of crocodile can apply 5,000 pounds of pressure per square inch, in comparison to a human's jaw which can only produce, 100 pounds of pressure per square inch.
• Crocodiles hearing is so good, that they can hear their offspring’s call from inside their egg.
• Crocodiles can swim up to 20 mph (32 kph) , however on land, they can only run up to 11 mph (17.6 kph), and for short distances.
• Crocodiles can hold their breath underwater for approximately one hour.
**Species **
There are fourteen species of crocodiles found around the world.
Facts on a few different species:
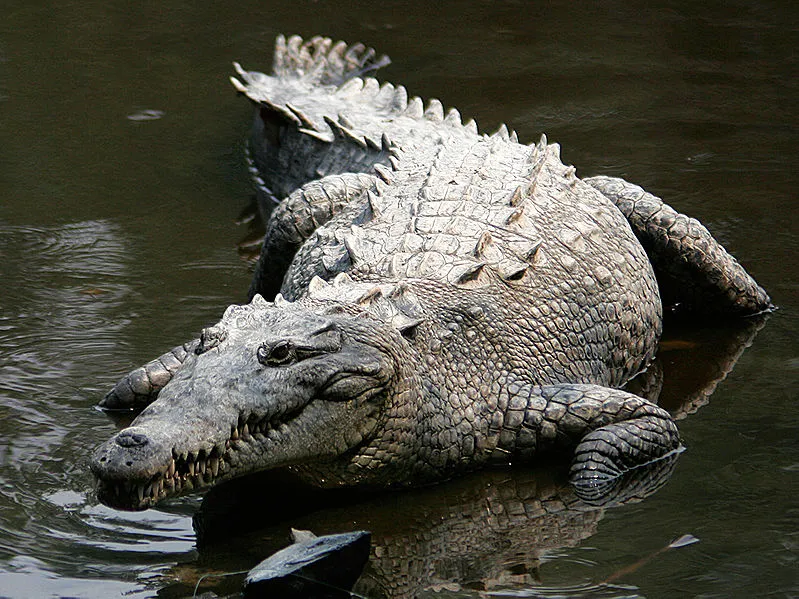
American Crocodile
This American Crocodile (Crocodylus acutus), can grow to approximately 15 feet long and can weigh up to 2000 pounds, however is sadly, considered to be vulnerable due to threats of poaching and habitat loss.
They can be found, living in the shores of the Americas, dwelling in a swampy habitats.
Their preferable habitat is the fresh or brackish water of river estuaries, coastal lagoons, and mangrove swamps; swamps of the Everglades in particular.
They can reach maximum speeds up to 32 km/h, in water.
Nile Crocodile
Nile crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus), are the largest of all members of the crocodile family, called crocodilians, which consists of crocodiles and alligators, with an average length of approximately 16 feet and weights between 500-1 200 pounds.
The Nile crocodile. lives along the banks of the Nile River which is one of the longest rivers in the world. The Nile river runs throughout Africa from below the equator in Burundi north to the Mediterranean Sea.
The Nile crocodile can be found throughout the lower Nile Basin in sub-Saharan Africa as well as the northeast coast of Madagascar. They used to be found all over Africa, but now they are mainly found in southern and eastern Africa. In western Africa, their population has reduced as a result of the threat of poaching.
Similar to the American crocodile, the Nile crocodile prefers the habitat of rivers, freshwater marshes, and mangrove swamps, however different to the American crocodile, the Nile crocodile prefers freshwater locations, therefore is not typically found in the brackish or saltwater estuaries. The Omo River in Ethiopia is a much preferred habitat of the Nile Crocodile.
These crocodiles are man-eaters and are responsible for approximately 200 deaths per year. They primarily eat fish and insects when they are young but as they grow, they will eat anything that crosses their path eg. birds, hippos, antelope, buffalo, and zebras, including other crocodiles.
The crocodile, by use of its fast legs and large jaws, grips and drags its selected prey under water, then spins it around allowing flesh to easily break of the prey, for the crocodile to easily swallow. This spinning action is a method referred to as the “Death Roll”
They can reach maximum speeds of between 30 – 35 km/h, in water.
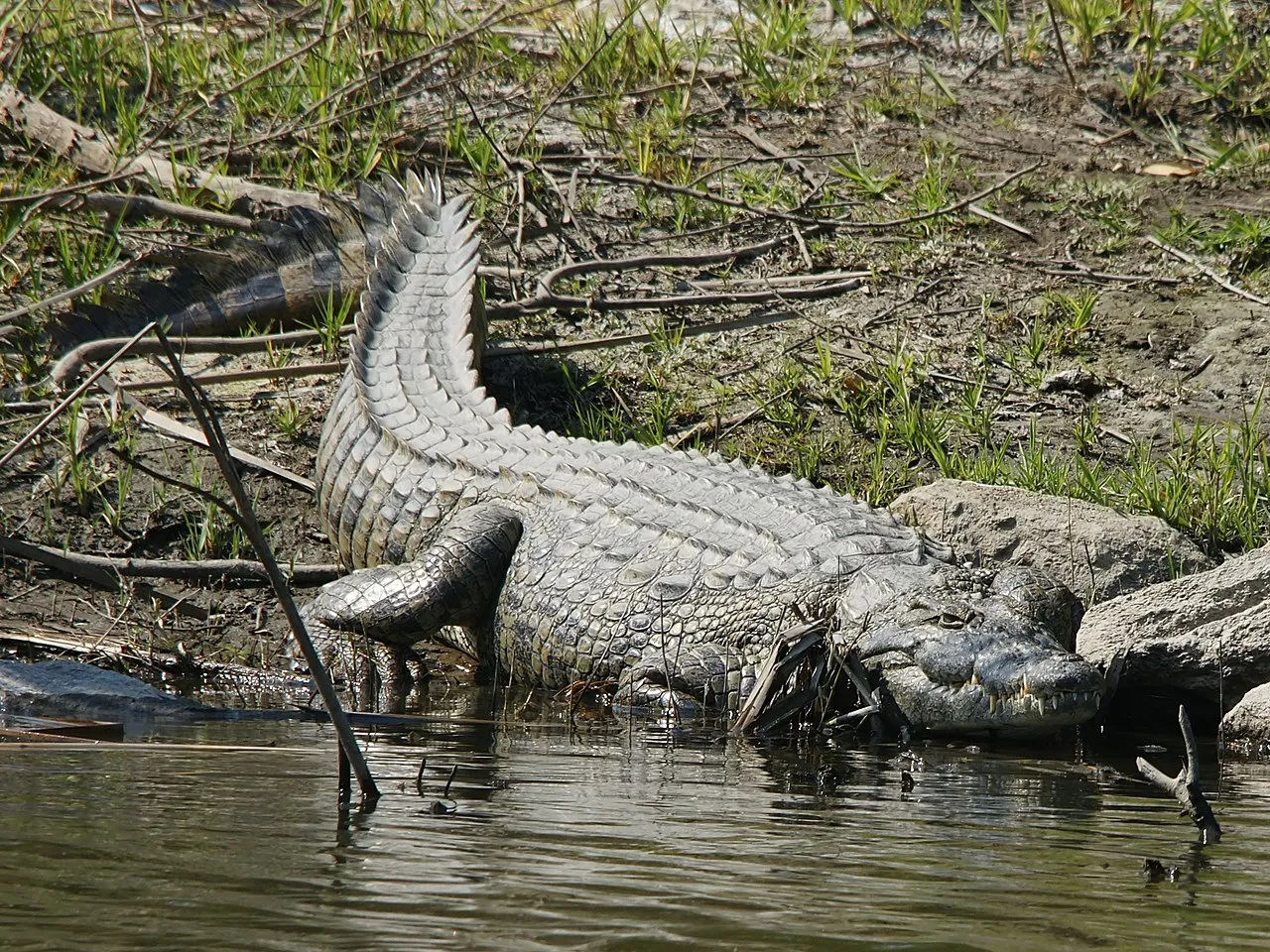
Saltwater Crocodile
The Saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus), lives in eastern India, Southeast Asia, and Northern Australia; in swamps, lakes, marshes, coastal waters, and estuaries. These colossal reptiles can measure from 16-23 feet in length, and can weigh between 1 000 - 2 000 pounds.
Saltwater crocodiles are often referred to as, estuarine crocodiles because their preferred habitat is estuaries.
An average male can grow to be about 17 feet long and can weigh up to approximately half of a ton. The females can grow up to 10 feet long.
They have wide snouts and powerful jaws, filled with teeth. They have webbed feet and long, powerful tails which helps the crocodile move through the water, which makes them very good swimmers and can even travel far out into the sea.
They have dark grey skin on their backs, with white or light grey, bellies.
A saltwater crocodile lies still just below the surface of the water, when it is on the hunt, it. It’s dark grey back peaking above the surface, appears only a harmless rock to the bypassing animal, allowing it to surprise and catch prey like buffalo, monkeys, dingoes, cattle, dogs, birds, and occasionally people. Sharks are also on their menu.
These reptiles are well-known to use their powerful legs and tail to explode from the water and grab their prey and drag them below the water, with their powerful jaws.
They can reach maximum speeds of between 24 – 29 km/h, in water.
Conservation status
The Cuban crocodile is considered critically endangered and has a population of only about 4,000, making it the world’s most endangered species of crocodile, as a result of the constant threat of poaching and habitat loss. The American crocodile is also measured as vulnerable.
Conclusion
For more on my series on amazing life in the water, on land & astoundingly parading the air, please follow me.
Thank You!
References:
https://www.livescience.com/28306-crocodiles.html
http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/life/Crocodylus
https://www.aboutanimals.com/reptile/nile-crocodile/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crocodile
All images are linked to their sources.