Stairs give access from floor to floor. The space/room housing stairs is called staircase. Stairs consists of a number of steps arranged in a single flight or more number of flights.
The requirement of good stairs are
a) Width: 0.9 m in residential buildings and 1.5 m to 2.5 m in public buildings.
(b) Number of Steps in a Flight: Maximum number of steps in a flight should be limited to 12 to 14, while minimum is 3.
(c) Rise: Rise provided should be uniform. It is normally 150 mm to 175 mm in residential
buildings while it is kept between 120 mm to 150 mm in public buildings. However in
commercial buildings more rise is provided from the consideration of economic floor area.
(d) Tread: Horizontal projection of a step in a stair case is called tread. It is also known as going.
In residential buildings tread provided is 250 mm while in public buildings it is 270 mm to 300 mm.
The following empirical formula is used to decide rise and tread:
2R + T > 550 mm but < 700 to 600 mm
whereR is rise in mm and T is tread in mm.
(e) Head Room: Head room available in the stair case should not be less than 2.1 m. (f) Hand Rails: Hand rails should be provided at a convenient height of a normal person which is from 850 mm to 900 mm.
Types of Stairs
The stairs may be built with wood, concrete masonry or with cast iron. Wooden stairs are not safe,
because of the danger of fire. However they are used in unimportant buildings to access to small areas
in the upper floors. Cast iron or steel stairs in the spiral forms were used commonly to reduce stair case
area. In many residential buildings masonry stairs are also used. Reinforced concrete stairs are very
commonly used in all types of buildings.
Based on the shapes stairs may be classified as:
(a) Straight stairs
(b) Dog legged stairs
(c) Well or open-newel stairs
(d) Geometrical stairs
(e) Spiral stairs
(f) Turning stairs.
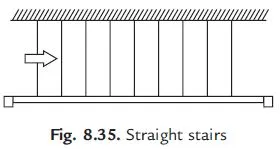
(a) Straight Stairs: If the space available for stair case is narrow and long, straight stairs may be provided. Such stairs are commonly used to give access to porch or as emergency exits to cinema halls. In this type all steps are in one direction. They may be provided in single flight or in two flights with landing between the two flights [Fig. 8.35].
Dog Legged Stairs: It consists of two straight flights with 180° turn between the two. They are very commonly used to give access from floor to floor. Figure 8.36 shows the arrangement of steps in such stairs.
(c) Well or Open-newel Stairs: It differs from dog legged stairs such that in this case there is
0.15 m to 1.0 m gap between the two adjacent flights. Figure 8.37 shows a typical opennewel stair.
(d) Geometrical Stair: This type of stair is similar to the open newel stair except that well formed between the two adjacent flights is curved. The hand rail provided is continuous. [Ref. Fig. 8.38]
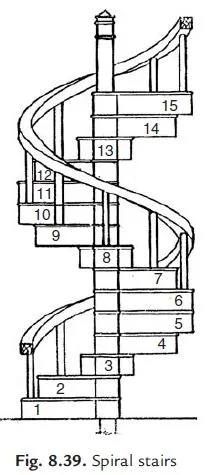
(e) Spiral Stairs: These stairs are commonly used as emergency exits. It consists of a central post supporting a series of steps arranged in the form of a spiral. At the end of steps continuous hand rail is provided. Such stairs are provided where space available for stairs is very much limited. Figure 8.39 shows a typical spiral stair. Cast iron, steel or R.C.C. is used for building these stairs.
( f ) Turning Stairs: Apart from dog legged and open newel type turns, stairs may turn in various forms. They depend upon the available space for stairs. Quarter turned, half turned with few steps in between and bifurcated stairs are some of such turned stairs. Figure 8.40 shows a bifurcated stair.
Salient Points to be Considered in Locating Stairs
The following points should be considered in locating stairs in a building:
(a) They should be located near the main entrance to the building.
(b) There should be easy access from all the rooms without disturbing the privacy of the rooms.
(c) There should be spacious approach.
(d) Good light and ventilation should be available.