
The concept of “Layer 2 blockchain technology” is starting to gain steam.
The early years of this industry have seen countless products attempt to use blockchain as a technical solution to their problem. Some of these solutions have been successful, while others have run up against some of blockchain’s native limitations.
Scale is the big issue, with root blockchains like Ethereum only able to process a paltry 15–20 transactions per second.
There are other issues as well, including high gas prices and questionable privacy. Root blockchains could theoretically implement changes that solve these issues, but it would almost always come at the cost of decentralization — the raison d’etre for using blockchain in the first place.
So how do we implement blockchain solutions for scale, privacy, and cost effectiveness without sacrificing decentralization?
That’s where Layer 2 blockchain tech comes in.
What is Layer 2 Blockchain Technology?
Layer 2 blockchain technology is often referred to as an “off-chain” solution. Its main purpose is to scale blockchain transaction capacity while retaining the decentralization benefits of a distributed protocol.
Solving the scalability problem will significantly help with blockchain mainstream adoption.
To build a good blockchain ecosystem, we need a few things in the architecture to balance the needs of security, decentralization, and scalability. Layer 2 blockchain technology systems are those that connect to say, Ethereum, and rely on Ethereum as a base layer of security and finality.
In other words, rather than changing the base Ethereum, we add smart contracts on the main blockchain protocol that interact with activities off-chain.
Source: Josh Stark, “Making Sense of Ethereum’s Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: State Channels, Plasma, and Truebit”
How does Layer 2 blockchain technology work?
Layer 2 platforms and protocols process data in a way that decreases the burden the base layer (root chain) usually bears. By offloading transactions from the main chain onto layer 2 platforms, the blockchain network can handle much higher transaction throughput.
What does Layer 2 technology enable that Layer 1 alone can’t do?
Blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum face inherent scaling limitations.
Ethereum processes roughly 15–20 transactions/second compared to Paypal and Visa with several hundred transactions/second and several thousand transactions/second, respectively.
Why does this blockchain architecture lag in processing?
When a transaction happens, there has to be global consensus across the decentralized network. All nodes on the network keep a full copy of the transactions to validate the transactions on the network. It’s designed to solve the double spend problem without relying on a middleman.
Blockchain networks can serve as the layer 1 (i.e. base layer) of the decentralized web ecosystem. The end goal is to ‘re-decentralize’ the infrastructure, protocols, applications and various layers of the world wide web.
Solutions are tiered. Layer 1 serves as the security layer that anchors data transaction in a way that’s immutable, cryptographically secured without a central authority. Elizabeth Starks of Lightning Labs refers to blockchains as“the base layer for the decentralized Internet.”
Layer 2 allows you to massively cut down data processing on the blockchain by running computations off-chain. The base chain will still be the ultimate judge (arbiter) when there are disputes (this is cryptoeconomics after all).
The main benefit of second layer is that it minimizes the amount of data storage on the base layer. Taking transactions off the base layer, while still anchored to it, would free up processing resources to do other things while still getting the security and decentralization benefits.
What does layer 2 blockchain tech mean for the industry moving forward?
Blockchain is a system evolving into multiple layers.
Layer 1 is the base layer (or root chain), followed by layer 2, eventually layer 3, and so on (yes, even Layer 3!). So on the top of the base layer are extensions such as 2nd layer solutions like Plasma, Sharding, and State Channels, followed by an array of decentralized applications.
For example, in the Lucidity architecture, the Ethereum blockchain is our base, root layer. The Lucidity Protocol would be like the HTTP, Blockstack, or Lightning Network that sits on top of the main Ethereum chain. On top of the base we’re using Plasma to build sidechains. The top most layer will be Lucidity applications as well as other industry applications built by our partners.
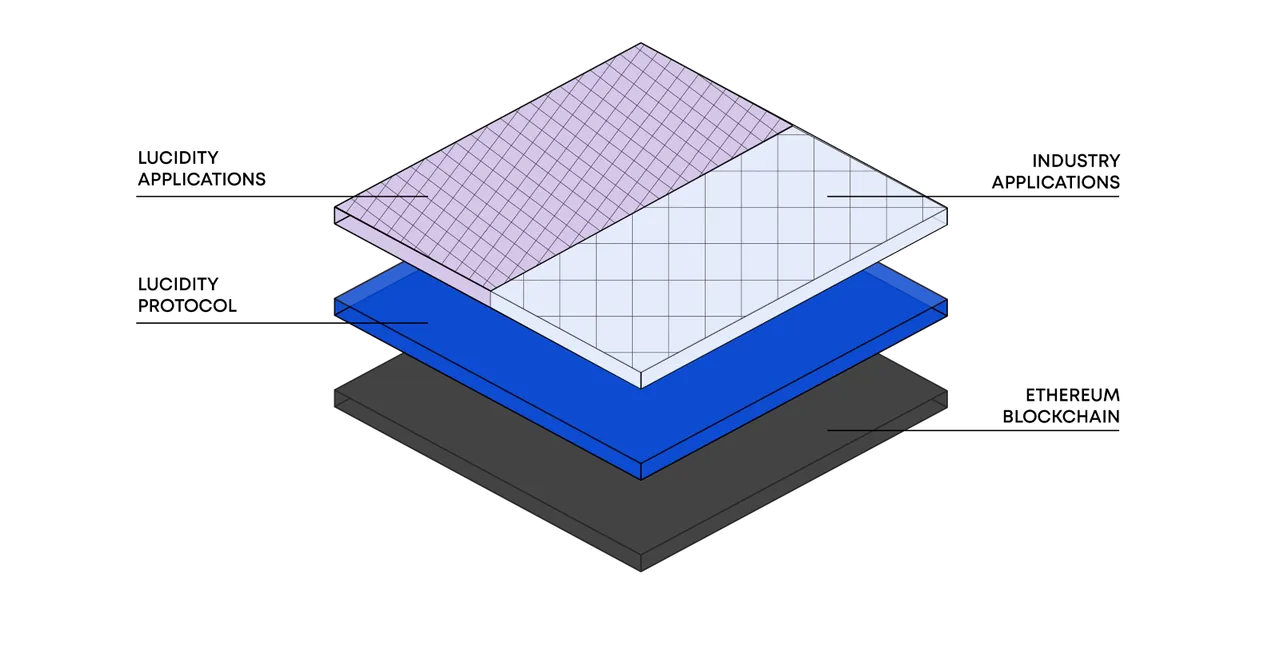
Essentially we’ve built a blockchain system that can match the speed and scale of programmatic advertising — and can now be used for other industries with high data processing needs.
So what are the implications for Layer 2 blockchain technology?
Layer 2 tech will help us create blockchain systems that are usable, that can scale with whatever industry they’re implemented for, and that can compete with the likes of established, centralized systems like Visa.
Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum, went ahead and did the math for us. Here’s the rough calculation he gave during a recent AMA session:
“If you look at the math, the scalability gains from the layer 1 improvements and layer 2 improvements do ultimately multiply up with each other. If you have a sharding solution, then the sharding solution itself might increase the scalability of Ethereum by a factor of 100, or eventually even more.But then, if you implement Plasma on top of the scalability solution, then what that means is you’re not just doing 100 times of the amount of activity but you are also doing 100 times the amount of entrances, 100 times the amount of exits, and 100 times the amount of dispute resolutions. All of that improves the number of users a system can handle, the number of disputes a system can handle, and ultimately the maximum safe capacity that the layer 2 system can handle by a factor of 100 as well.
So if we get 100x from sharding and 100x from Plasma, the two together basically give you a 10,000x scalability gain. Which does mean that blockchains will be powerful enough to handle most applications people are trying to do with them.”
Join us on Telegram → https://t.me/luciditytech
Check out our whitepaper → https://lucidity.tech/whitepaper/
Follow us on Twitter → https://twitter.com/lucidity_tech
Join our community on Facebook → https://www.facebook.com/luciditytech/
Or follow us on LinkedIn → https://www.linkedin.com/company/luciditytech/
Originally published at lucidity.tech on July 12, 2018.